CHAPTER 10
MULTIBUS
'II
AND Intel386
OX
MICROPROCESSOR
Standard bus interfaces guarantee compatibility between existing and
newly
developed
systems. This compatibility safeguards a user's hardware investment against
obsoles-
cence even in the face
of
rapidly advancing technology. The MULTIBUS I standard
interface has proven its value in providing flexibility for the expansion of existing systems
and the integration of
new
designs. The MULTIBUS II standard interface extends
Intel's
Open Systems design strategy into the world
of
32-bit microprocessing systems.
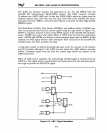
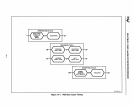
10.1 MULTIBUS II STANDARD
The MULTIBUS II standard
is
a processor-independent bus architecture that features a
32-bit parallel system bus with a maximum throughput of
40
megahytes per
second~
high-speed local bus access to off-board memory, a low-cost serial system bus, and full
multiprocessing support.
MULTIBUS II achieves these features through
five
specialized
Intel buses:
• Parallel System Bus (iPSB)
•
Local Bus Extension (iLBX II)
• Serial System Bus (iSSB)
•
Multi-channel DMA 110 Bus
• System Expansion I/O Bus
(iSBXTM)
The DMA I/O Bus and
the.
iSBX are carried over directly from MULTIBUS I architec-
ture. See the
MULTIBUS~
I Architectural Specification for a full description
of
these
buses. The multiple
bus structure provides the following important advantages over a
single, generalized bus:
• Each bus
is
optimized
fora
specific function.
• The buses perform operations in parallel.
• Buses that are not needed for a particular system can be omitted, avoiding unneces-
sary costs.
10.2 PARALLEL SYSTEM BUS (iPSB)
The Parallel System Bus (iPSB)
is
optimized for interprocessor data transfer and com-
munication. Its burst transfer capability provides a maximum sustained bandwidth of
40
megabytes per second for high-performance data transfers.
10-1