COPROCESSOR HARDWARE INTERFACE
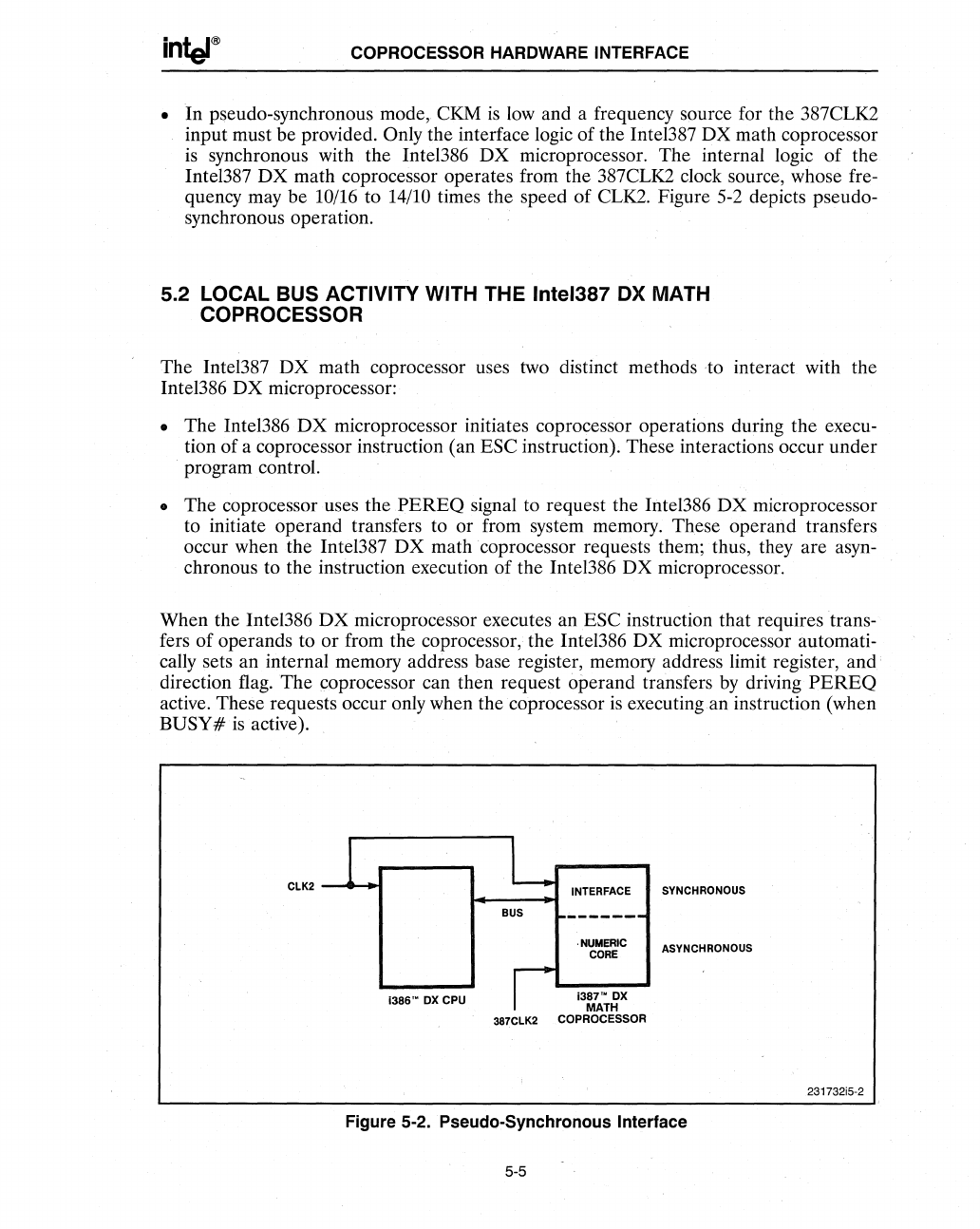
• In pseudo-synchronous mode, CKM
is
low and a frequency source for the 387CLK2
input must be provided.
Only the interface logic of the Intel387 DX math coprocessor
is
synchronous with the Inte1386 DX microprocessor. The internal logic
of
the
Intel387
DX
math coprocessor operates from the 387CLK2 clock source, whose fre-
quency may be 10/16 to 14/10 times the speed of CLK2. Figure
5-2
depicts pseudo-
synchronous operation.
5.2 LOCAL BUS ACTIVITY WITH THE Intel387
OX
MATH
COPROCESSOR
The Inte1387
DX
math coprocessor uses two distinct methods
,to
interact with the
Intel386
DX
microprocessor:
• The Inte1386
DX
microprocessor initiates coprocessor operations during the execu-
tion of a coprocessor instruction (an ESC instruction). These interactions occur under
program control.
• The coprocessor uses the
PEREQ
signal to request the Inte1386
DX
microprocessor
to initiate operand transfers to or from system memory. These operand transfers
occur when the Intel387
DX
math coprocessor requests them; thus, they are asyn-
chronous to the instruction execution of the Intel386
DX
microprocessor.
When the Inte1386
DX
microprocessor executes an ESC instruction that requires trans-
fers of operands to or from the coprocessor, the Intel386 DX microprocessor automati-
cally sets an internal memory address base register, memory address limit register,
and'
direction flag.
The
(;oprocessor can then request operand transfers
by
driving
PEREQ
active. These requests occur only when the coprocessor
is
executing an instruction (when
BUSY #
is
active).
CLK2
- ...........
i386~
ox
CPu
INTERFACE
.
NUMERIC
CORE
i387'·
ox
MATH
387CLK2
COPROCESSOR
SYNCHRONOUS
ASYNCHRONOUS
Figure 5-2. Pseudo-Synchronous Interface
5-5
231732iS-2
