MULTIBUS I AND Intel386
DX
MICROPROCESSOR
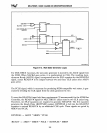
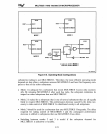
9.4.3 MULTIBUS I Locked Cycles
Locked bus cycles for the local bus are described in Chapter
3.
In locked bus cycles, the
Intel386
OX
microprocessor asserts the
LOCK#
signal to prevent another bus master
from intervening between two bus cycles. In the same manner, an Intel386
OX
micro-
processor processing subsystem can assert the
LLOCK#
output of its bus arbiter to
prevent other subsystems from gaining control of MULTIBUS
1.
A locked cycle over-
rides the normal operating mode of the bus arbiter (one of the four modes mentioned in
Section 9.4.2.
Locked MULTIBUS I cycles are typically used to implement software semaphores
(described in Section 3.5) for critical code sections or critical real-time events. Locked
cycles can also be used for high-performance transfers within one instruction.
The Intel386
OX
microprocessor
initiatesalocked
MULTIBUS I cycle
by
asserting its
LOCK#
output to the 82289 bus arbiter. The bus arbiter outputs its LLOCK# signal to
the MULTIBUS I
LOCK#
status line and holds
LLOCK#
active until the
LOCK#
signal from the Intel386
OX
microprocessor goes inactive. The
LLOCK#
signal from the
bus arbiter must be connected to the MULTIBUS I
LOCK#
status line through a
tristate driver controlled
by
the
AEN#
output of the bus arbiter.
9.5 OTHER MULTIBUS I DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Additional design considerations are presented in this section. These considerations
include provisions for interrupt handling, 8-bit transfers, timeout protection, and power
failure handling on MULTIBUS
1.
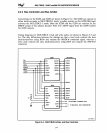
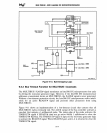
9.5.1 Interrupt-Acknowledge
on
MULTI
BUS
I
When an interrupt
is
received
by
the Intel386
OX
microprocessor, the Intel386
OX
microprocessor generates an interrupt-acknowledge cycle (described in Chapter 3) to
fetch an 8-bit interrupt vector from the 8259A Programmable Interrupt Controller. The
8259A can be located on either
MUL TIBUS
lora
local bus.
Multiple 8259As can be cascaded (one master and up to eight slaves) to process up to
64
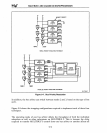
interrupts. Three configurations are possible for cascaded interrupt controllers:
• All of the interrupt controllers for one
Intel386OX
microprocessor reside on the
local bus of that processor, and all interrupt-acknowledge cycles are directed to the
local bus.
• All slave interrupt controllers (those that connect directly to interrupting devices)
reside on MULTIBUS
1.
The master interrupt controller may reside on either the
local bus
or
MULTIBUS
1.
In
this case, all interrupt-acKnowledge cycles are directed
to MULTIBUS
1.
9-14