SA-1100 Developer’s Manual 1-5
Introduction
The instruction set comprises eight basic instruction types:
• Two make use of on-chip arithmetic logic unit, barrel shifter, and multiplier to perform
high-speed operations on data in a bank of 16 logical registers (31 physical registers), each 32
bits wide.
• Three classes of instructions control data transfer between memory and the registers: one
optimized for flexibility of addressing, one for rapid context switching, and one for swapping
data.
• Two instructions control the flow and privilege level of execution.
• One class is used to access the privileged state of the CPU.
The ARM instruction set is a good target for compilers of many different high-level languages.
Where required for critical code segments, assembly code programming is also straightforward,
unlike some RISC processors that need sophisticated compiler technology to manage complicated
instruction interdependencies.
The SA-1100 is a static part and has been designed to run at a reduced voltage to minimize its power
requirements. This makes it a good choice for portable applications where both of these features are
essential.
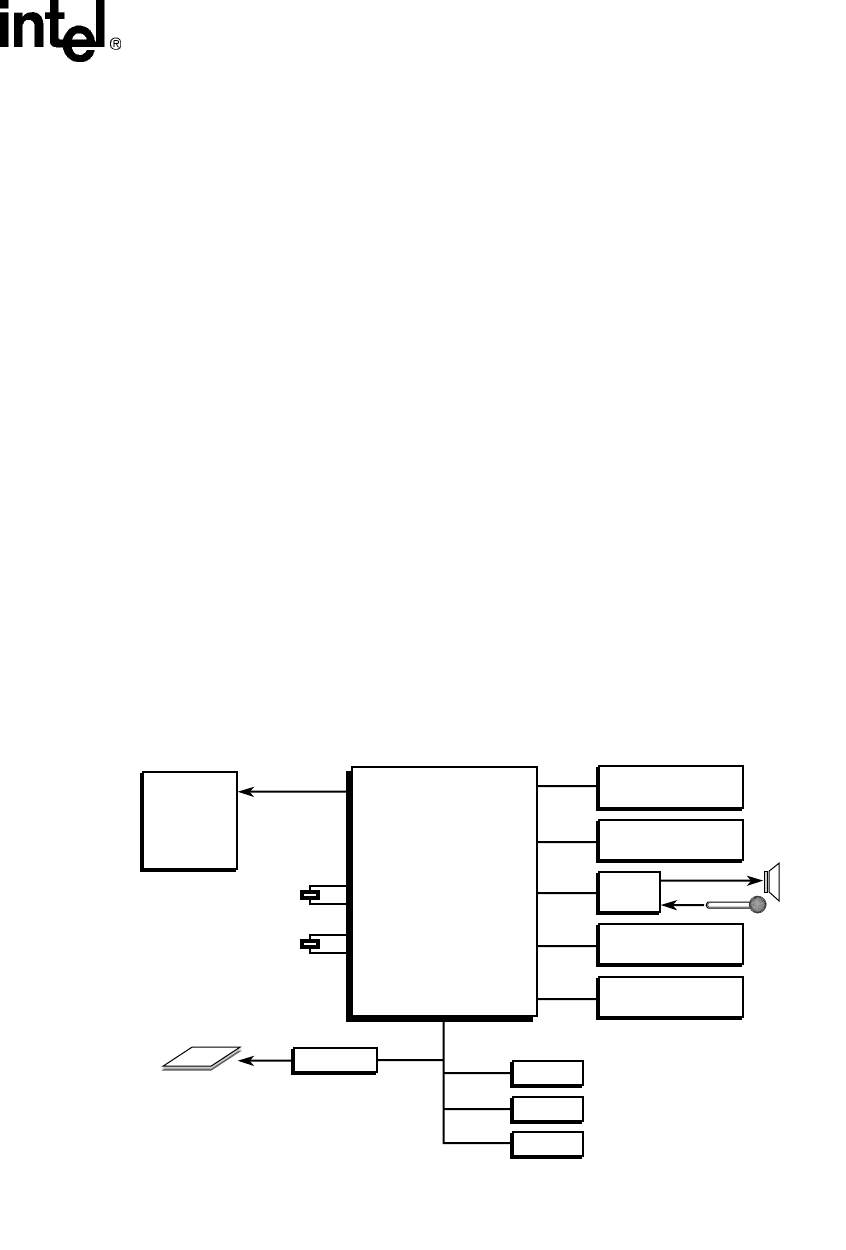
1.3 Example System
Figure 1-2 shows how the SA-1100 can be used in a hand-held computing device.
Figure 1-2. SA-1100 Example System
A6870-01
32.768
KHz
3.686
MHz
Intel
®
StrongARM
®*
SA-1100
Portable
Communications
Microcontroller
UART or LocalTalk
Communications
Tablet / Serial
Keyboard
Infrared
Communications
USB Synchronization
Port
Codec
Flash
ROM
DRAM
Glue Logic
PCMCIA Interface
(Flash, Modem)
Gray Scale
or
Color LCD
Display
* StrongARM is a registered trademark of ARM Limited.


















