System Management: IPMB Protocol
10007175-02 KAT4000 User’s Manual
9-5
IPMB PROTOCOL
The IPMB message protocol is designed to be robust and support many different physical
interfaces. The IPMC supports messages over the IPMB interface. Messages are defined as
either a request or a response, as indicated by the least significant bit in the Network Func-
tion Code of the message.
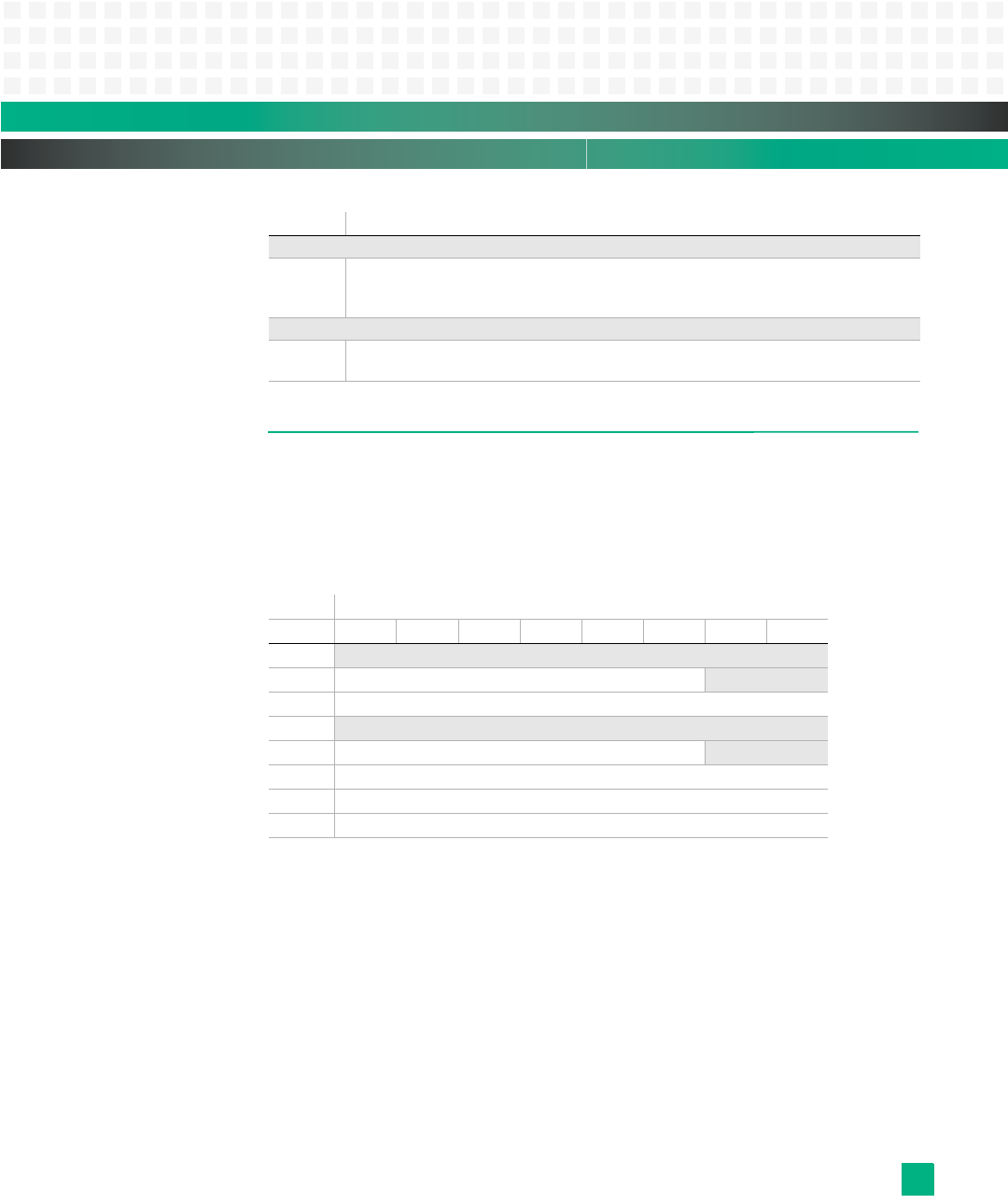
Tab le 9 -3 shows the format of an IPMI request message followed
by each byte description.
Table 9-3: Format for IPMI Request Message
• The first byte contains the responder’s Slave Address, rsSA.
• The second byte contains the Network Function Code, netFn, and the responder’s
Logical Unit Number, rsLUN.
• The third byte contains the two’s-complement checksum for the first two bytes.
• The fourth byte contains the requester’s Slave Address, rqSA.
• The fifth byte contains the requester’s Sequence Number, rqSeq, and requester’s
Logical Unit Number, rqLUN. The Sequence number may be used to associate a specific
response to a specific request.
• The sixth byte contains the Command Number.
Device-Specific (OEM) Codes 01-7E
01-7E Device specific (OEM) completion codes–command-specific codes (also specific for a
particular device and version). Interpretation of these codes requires prior knowledge
of the device command set.
Command-Specific Codes 80-BE
80-BE Standard command-specific codes–reserved for command-specific completion codes
(described in this chapter)
Byte: Bits:
76543210
1
rsSA
2
netFn rsLUN
3
Checksum
4
rqSA
5
rqSeq rqLUN
6
Command
7:N
Data
N+1
Checksum
Code: Description: (continued)


















