Epson Research and Development
Page 33
Vancouver Design Center
Programming Notes and Examples S1D13505
Issue Date: 01/02/05 X23A-G-003-07
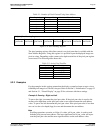
Figure 5-4: Pixel Panning Register
The pixel panning register offers finer control over pixel pans than is available with the
Start Address Registers. Using this register it is possible to pan the displayed image one
pixel at a time. Depending on the current color depth certain bits of the pixel pan register
are not used. The following table shows this.
5.2.2 Examples
For the examples in this section assume that the display system has been set up to view a
640x480 pixel image in a 320x240 viewport. Refer to Section 2, “Initialization” on page 12
and Section 5.1, “Virtual Display” on page 29 for assistance with these settings.
Example 3:Panning - Right and Left
To pan to the right, increment the pixel pan value. If the pixel pan value is equal to the
current color depth then set the pixel pan value to zero and increment the start address
value. To pan to the left decrement the pixel pan value. If the pixel pan value is less than
zero set it to the color depth (bpp) less one and decrement the start address.
Note
Scrolling operations are easier to follow if a value, call it pan_value, is used to track
both the pixel pan and start address. The least significant bits of pan_value will repre-
sent the pixel pan value and the more significant bits are the start address value.
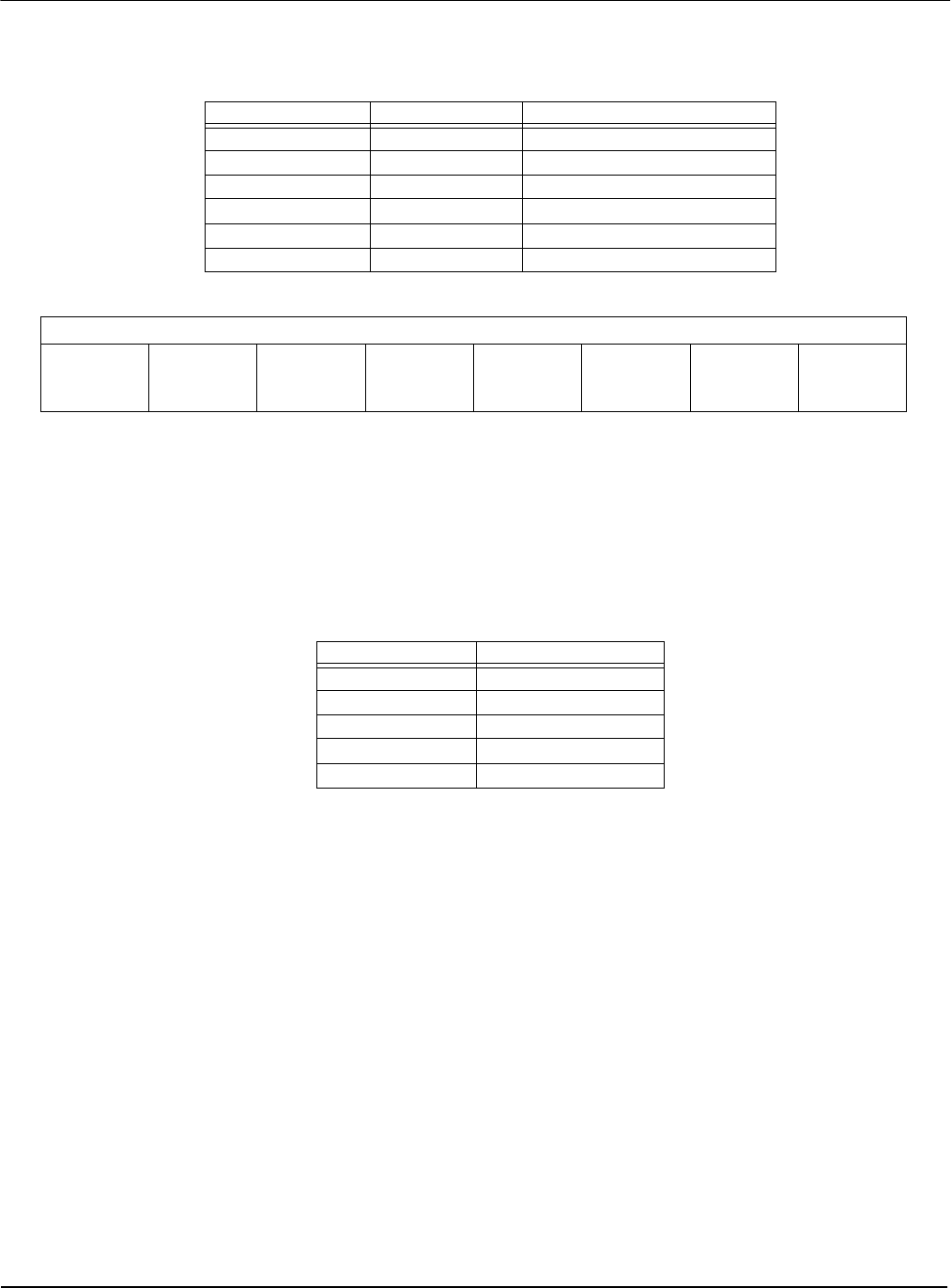
Table 5-1: Number of Pixels Panned Using Start Address
Color Depth (bpp) Pixels per Word Number of Pixels Panned
116 16
28 8
44 4
82 2
15 1 1
16 1 1
REG[18h] Pixel Panning Register
Screen 2
Pixel Pan Bit
3
Screen 2
Pixel Pan Bit
2
Screen 2
Pixel Pan Bit
1
Screen 2
Pixel Pan Bit
0
Screen 1
Pixel Pan Bit
3
Screen 1
Pixel Pan Bit
2
Screen 1
Pixel Pan Bit
1
Screen 1
Pixel Pan Bit
0
Table 5-2: Active Pixel Pan Bits
Color Depth (bpp) Pixel Pan bits used
1bits [3:0]
2bits [2:0]
4bits [1:0]
8bit 0
15/16 ---