15
CONFIGURING ISDN PROTOCOL
This chapter contains information on the following topics:
■ ISDN Overview
■ Configure ISDN
■ Display and Debug ISDN
■ Typical Configuration Example
■ Fault Diagnosis and Troubleshooting of ISDN
ISDN Overview ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network), developed from telephone integrated
digital network (IDN), provides end-to-end digital connection, so as to support
wide range of services (including voice and non-voice services).
ISDN provides the user with a group of standard multifunctional user-network
interfaces. In ITU-T I.412 recommendations, two types of user-network interfaces
are specified: Basic Rate Interface (BRI) and Primary Rate Interface (PRI). The
bandwidth of BRI is 2B+D, and that of PRI is 30B+D or 23B+D. Here:
■ B channel is a user channel, used to transmit the voice, data and other user
information with the transmission rate 64kbps.
■ D channel is a control channel and used to transmit the common channel
signaling, controlling the calls on B channels of the same interface. The rate of
D channel is 64kbit/s (PRI) or 16kbps (BRI).ITU-T Q.921, the data link layer
protocol of D channel, defines the rules by which the information is exchanged
between layer-2 entities on the user-network interface through D channel.
Meanwhile, it supports the access of layer-3 entity. ITU-T Q.931, the network
layer protocol of D channel, provides methods to establish, maintain and
terminate the network connection between communication application
entities.
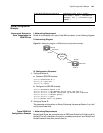
Figure 55 Protocol stack of ISDN D channel
Configure ISDN ISDN configuration includes:
■ Configure ISDN signaling type
■ Configure QSIG signaling parameters
BRI PRI
Q.921 LAPD
Q.931 QSIG
Layer 1
Layer 2
Layer 3