IKE Configuration Example 593
IKE Configuration
Example
■ Hosts A and B communicates securely, and a security channel is established
with IKE automatic negotiation between security gateways A and B.
■ Configure an IKE policy on Gateway A, with Policy 10 is of highest priority and
the default IKE policy is of the lowest priority.
■ Pre-shared key authentication algorithm is adopted.
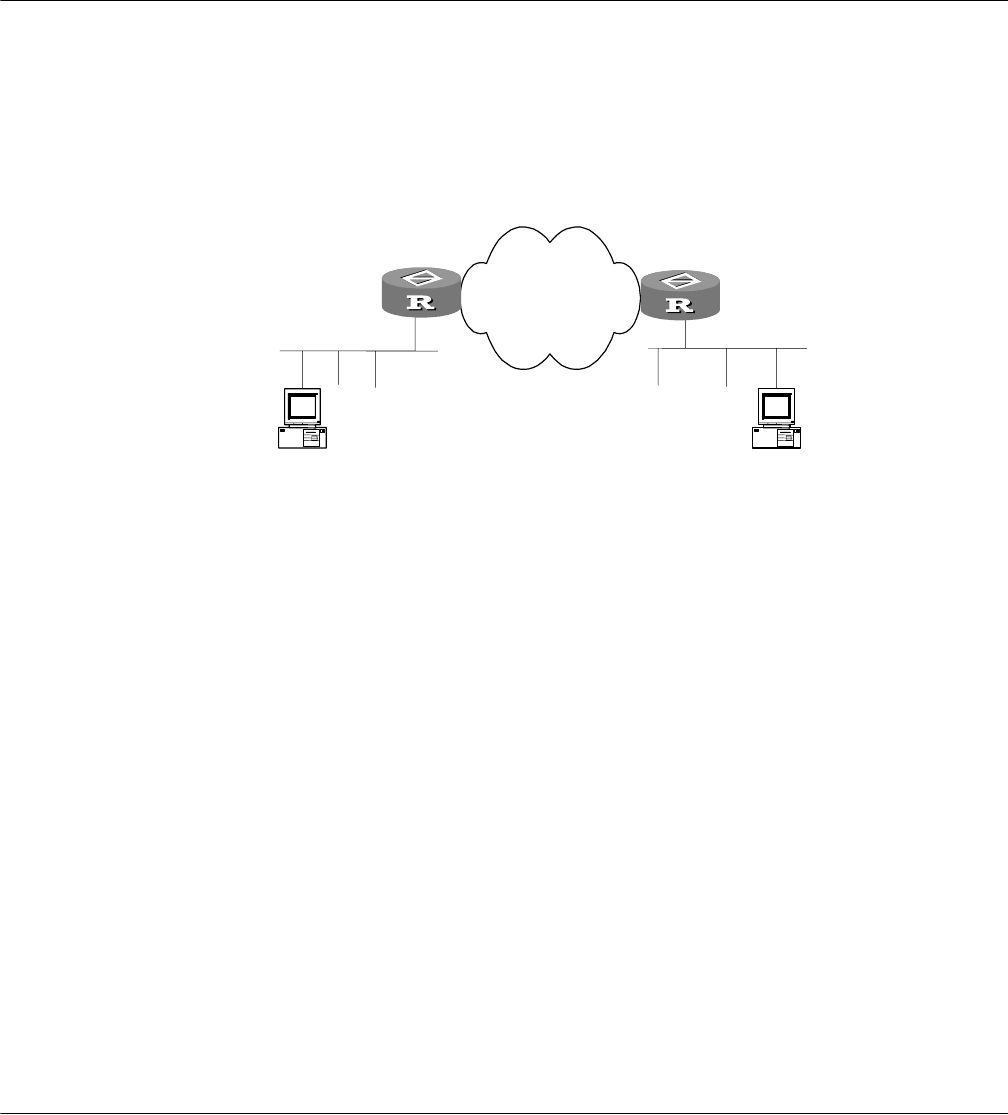
Figure 177 Networking diagram of IKE configuration example
1 Configure Security Gateway A.
a Configure a IKE Policy 10
[RouterA]ike proposal 10
b Specify the hashing algorithm used by IKE policy as MD5
[RouterA-ike-proposal-10] authentication-algorithm md5
c Use pre-shared key authentication method
[RouterA-ike-proposal-10] authentication-method pre-share
d Configure “abcde” for peer 171.69.224.33
[RouterA] ike pre-share-key abcde remote 171.69.224.33
e Configure IKE SA lifetime to 5000 seconds
[RouterA-ike-proposal-10] sa duration 5000
2 Configure Security Gateway B.
a Use default IKE policy on Gateway B and configure the peer authentication
word.
[RouterB] ike pre-share-key abcde remote 202.38.160.1
These steps configure IKE negotiation. To establish an IPSec security channel for
secure communication, it is necessary to configure IPSec correspondingly. For
detailed contents, see the configuration examples in IPSec Configuration.
Troubleshooting IKE When configuring parameters to establish IPSec security channel, you can use the
debugging ike error command to enable error debugging of IKE.
Invalid user ID information
User ID information is the data for the user originating IPSec communication to
identify itself. In practical applications user ID establishes a different security path
Host BHost A
Security Gateway B
Internet
Security Gateway A
Serial 0
202.38.160.1
Serial 0
171.69.224.33


















