698 CHAPTER 50: CONGESTION AVOIDANCE
and it causes the sudden increase and decrease of the network traffic, and the line
traffic always fluctuates between the states of few or none and full.
RED and WRED RED and WRED can avoid global synchronization of TCP by dropping packets
randomly. When the packets of a TCP connection are dropped, and transmission
slows down, other TCP connections can still send packets at high rates, thus
improving the utilization of the bandwidth.
RED and WRED avoids the TCP global synchronization phenomenon through the
random drop packets--when the packet of a TCP connection is dropped and the
transmission speed is reduced, other TCP connections still have the higher
transmission speeds. Thus, it is always the case that some TCP connection
performs the faster transmission, increasing the use ratio of the line bandwidth.
Both RED and WRED compare between the queue length, and minimum and
maximum thresholds, to perform the drop (this is to set the absolute length of the
queue). It will cause the unfair treatment on the burst data flow and be
disadvantageous for the transmission of the data flow. Therefore, when
comparing the minimum and maximum thresholds, and when dropping, the
average lengths of the queue are adopted (this is to set the relative value of the
comparison between the queue threshold and the average length). The average
length of the queue is the result of the low pass filtering of the queue length, it
reflects the variation trend of the queue, and is not sensitive to the burst change
of the queue length, so as to avoid the unfair treatment on the burst data flows.
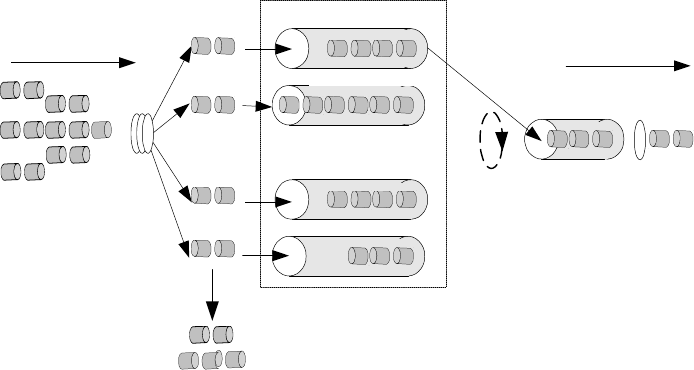
The relationship between WRED and queue mechanism is shown in Figure 223
Figure 223 Schematic diagram of the relationship between WRED and queue mechanism
In the RED class algorithm, a pair of minimum threshold and maximum threshold is
set for each queue, and the following specification is set:
■ When the length of the queue is less than the minimum threshold, no packet is
dropped.
■ When the length of the queue is larger than the maximum threshold, all
incoming packets are dropped.
incoming packets
queue1 weight1
queue2 weight2
classify
outgoing packets
queueN-1 weightN-1
queueN weightN
transmit
queue
interface
¡-¡-
scheduler
¡-¡-
WRED drop
Discarded
packets


















