588 CHAPTER 41: CONFIGURING IKE
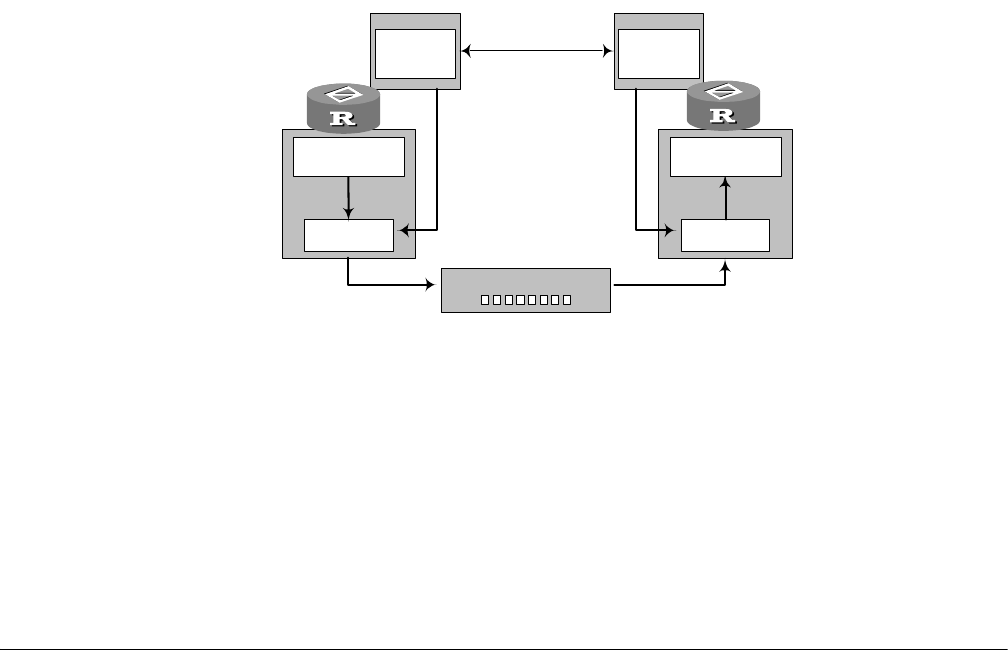
Figure 176 Diagram of relationship between IKE and IPSec
IKE features ■ Avoid specifying manually all IPSec security parameters in password mapping of
both communication ends.
■ Allow specifying the lifetime of IPSec SA
■ Allow exchanging ciphering key during IPSec session
■ Can provide anti-replay service by IPSec
■ Allow manageable and scalable IPSec to implement certificate authorization
support.
■ Allow dynamic end-to-end authentication.
Configuring IKE IKE configuration includes:
■ Creating an IKE Security Policy
■ Selecting an Encryption Algorithm
■ Selecting an Authentication Algorithm
■ Configuring Pre-shared Key
■ Selecting the Hashing Algorithm
■ Selecting DH Group ID
■ Setting the Lifetime of IKE Association SA
■ Configuring IKE Keepalive Timer
Creating an IKE Security
Policy
IKE negotiation determines whether IKE policies at both ends are matched and
then reach a negotiation using an IKE policy. During the subsequent negotiation,
the security data provided by this IKE policy will be used to protect negotiation
data.
Multiple policies with priority must be created on each terminal to ensure that at
least one policy can match that of the remote terminal.
■ Encryption algorithm: At present, it includes 56-bit DES-CBC (DES-Cipher Block
Chaining) algorithm and 168-bit 3DES-CBC algorithm.
TCP/UD
P
IPSec
IKEIKE
IPSec
TCP/UDP
SA SA
SA negotiation
Encrypted IP message
IP
Router B
Router A


















