434 CHAPTER 29: CONFIGURING OSPF
which reduces the LSDB in other areas. The configuration of range is only effective
when it is configured on teh ABR in the stub area.
For example, there are two network segments in an area as follows:
202.38.160.0 255.255.255.0
202.38.180.0 255.255.255.0
They are summarized into one network segment: 202.38.0.0 255.255.0.0
When the summary network segment of a specific network is added to an area,
the internal routes with the IP addresses that fall in this summary network
segment are not broadcast separately to other areas. Only the abstract
information of the route of the whole summary network segment is broadcast. If
the network segment range is restricted with the
notadvertise attribute, the
abstract information to this network segment route is not broadcast. This network
segment is described in the form of an IP address/mask. Receiving the summary
network segment and the restriction of the network segment can reduce the
inter-area routing information.
Note that the route summary is only effective when configured on an ABR.
Perform the following configurations in OSPF view.
Table 500 Configure Route Summarization Within OSPF Domain.
By default, inter-area routes are not summarized.
It must be noted that a routing summary configuration is only valid on the ABR.
Creating and
Configuring a Virtual
Link
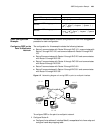
After the OSPF area division, all the areas may not be of equal size. One particular
area is unique and that is the backbone area with the area-id of 0.0.0.0. OSPF
route update between non-backbone areas is carried out through the backbone
area. The OSPF protocol requires that all non-backbone areas be connected to
backbone areas and at least one port on an ABR must be in the area 0.0.0.0. If
there is no physical connection between an area and the backbone area 0.0.0.0, a
virtual link must be created.
If a physical connection is not possible due to the limitation of the network
topology, a virtual link can satisfy this requirement. Virtual link refers to a logical
connection channel between two ABRs that is created through an area of
non-backbone area internal routes. Both ends of the virtual link must be ABRs and
both ends must be configured at the same time so that the virtual link can take
effect. A virtual link is flagged with the ID of the opposite router. The area
providing the non-backbone internal route for both ends of the virtual connection
is called a transit area, whose area-id must also be specified.
Operation Command
Configure route summarization within
OSPF domain.
abr-summary address mask mask area
area-id [ advertise | notadvertise ]
Cancel route summary between areas undo abr-summary address mask mask
area area-id