318 CHAPTER 20: CONFIGURING IP ADDRESS
The IP addresses a user can use are listed in the following table.
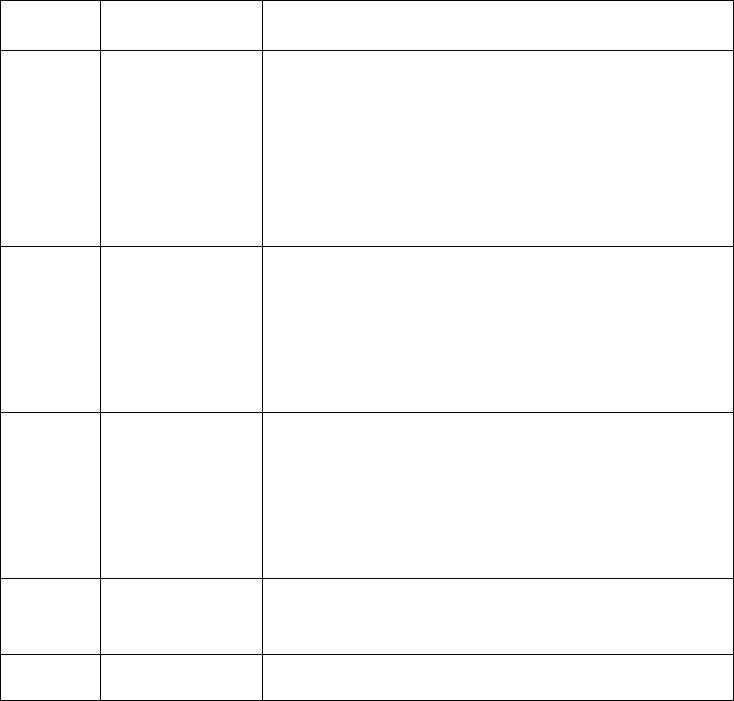
Table 351 IP address classes and ranges
Important features of IP address:
Some IP addresses are not in a hierarchical structure, which is different from the
structure of telephone number. In other words, these IP addresses cannot reflect
any geographical information about the host position.
■ When a host is connected to two networks at the same time (such as the host
used as a router), it must have two corresponding IP addresses with different
net-ids. Such host is called multihomed host.
■ According to Internet concept, several LANs connected via transceiver or
bridges are still in the same network, so these LANs have the same net-id.
■ In terms of IP address, all networks which are assigned with net-ids are equal
(no matter whether it is a small LAN or a big WAN).
Since 1985, only the net-id of IP address is assigned, while the following host-id is
controlled by the enterprise. The IP address assigned to an enterprise is only a
network ID: net-id. The specific host Ids, the host-ids for respective hosts, shall be
assigned by the enterprise independently and uniquely. If there are many
enterprise hosts widely scattered, the host IDs may be further divided into internal
sub-nets to facilitate management. Please note that the division of sub-nets is
Network
class
IP network range Description
A 1.0.0.0 ~ 126.0.0.0 Network IDs with all the digits being 0 or all the digits being
1 are reserved for special use.
Host ID with all the digits being 0 indicates that the IP
address is the network address, and is used for network
routing.
Host ID with all the digits being 1 indicates the broadcast
address, i.e. broadcast to all hosts on the network.
Network ID 127 is used for self-loop interface.
B 128.1.0.0 ~
191.254.0.0
Network IDs with all the digits being 0 or all the digits being
1 are reserved for special use.
Host ID with all the digits being 0 indicates that the IP
address is the network address, and is used for network
routing.
Host ID with all the digits being 1 indicates the broadcast
address, i.e. broadcast to all hosts on the network.
C 192.0.1.0 ~
223.255.254.0
Network IDs with all the digits being 0 or all the digits being
1 are reserved for special use.
Host ID with all the digits being 0 indicates that the IP
address is the network address, and is used for network
routing.
Host ID with all the digits being 1 indicates the broadcast
address, i.e. broadcast to all hosts on the network.
D None Addresses of class D are multicast addresses.
Host ID with all the digits being 1 indicates the broadcast
address, i.e. broadcast to all hosts on the network.
E None 255.255.255.255 is used as the whole network's broadcast
address, and the other addresses are reserved for future use.


















