X.25 and LAPB Protocols Overview 197
Once a virtual circuit is established between a pair of DTEs, it is assigned with a
unique virtual circuit number. When one DTE is to send a packet to the other, it
numbers this packet (with virtual circuit number) and sends it to DCE. According
to the number on the packet, DCE determines the method to switch this packet
within the switching network, so that this packet can reach the destination. Since
the X.25 layer 3 multiplexes the link established between DTE and DCE by the
X.25 layer 2 (LAPB), what finally viewed by the user will be multiple usable virtual
circuits.
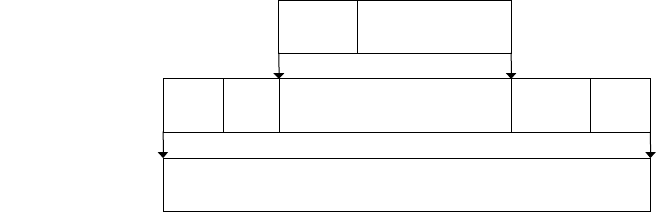
The relation between packets and frames in various X.25 layers is shown in the
following diagram.
Figure 60 X.25 packet and LAPB frame
X.25 link layer specifies the frame switching process between DTE and DCE. In
terms of hierarchy, the link layer seems to bridge the packet layer interface of DTE
and that of DCE. Through this bridge, the packets can be transmitted continuously
between the packet layer of DTE and that of DCE. The link layer has such main
functions as follows:
■ Transmit the data effectively between DTE and DCE
■ Ensure the synchronization of information between the receiver and
transmitter
■ Detect and correct the error in the transmission
■ Identify and report the procedure error to the higher layer protocol
■ Inform the packet layer of the link layer state
As specified in international standards, X.25 link layer protocol LAPB adopts the
frame structure of high-level data link control (HDLC) and the frame structure is a
subset of LAPB. The bi-directional link will be established when either site sends an
SABM (Set Asynchronous Balanced mode) command and the other replies with
UA.
Defined as X.25 layer-2 protocol, LAPB is actually a separate link layer protocol,
which can transmit the data with LAPB bearing non-X.25 upper layer protocol.
3Com Router
series can configure the link protocol of serial interface to LAPB and
perform simple local data transmission. Meanwhile, X.25 of 3Com Router series
has switching function, that is to say, the router can be used as a small X.25
packet switch. The following diagram shows the relations among LAPB, X.25 and
X.25 switching.
Packet
header
User data
Data
Frame
header
FCS
Frame
delimiter
Bit stream
X.25 layer 3 Packet
X.25 layer 2 Frame
X.25 layer 1
Frame
delimiter