20
CONFIGURING IP ADDRESS
This chapter contains information on the following topics:
■ IP Address Overview
■ Troubleshooting IP Address Configuration
■ Map between WAN Interface IP Address and Link Layer Protocol Address
IP Address Overview IP address is a unique 32-bit address assigned to a host connected to Internet.
Usually it is composed of two parts: network ID and host ID. Its structure enables
convenient addressing on Internet. IP address is assigned by Network Information
Center (NIC) of American National Defense Data Network.
For easy IP address management and convenient networking, IP address of
Internet is divided into five classes. An IP address consists of the following 3 fields:
■ Type field (also called type bit), used to distinguish the type of IP address.
■ Network ID field (net-id).
■ Host ID field (host-id).
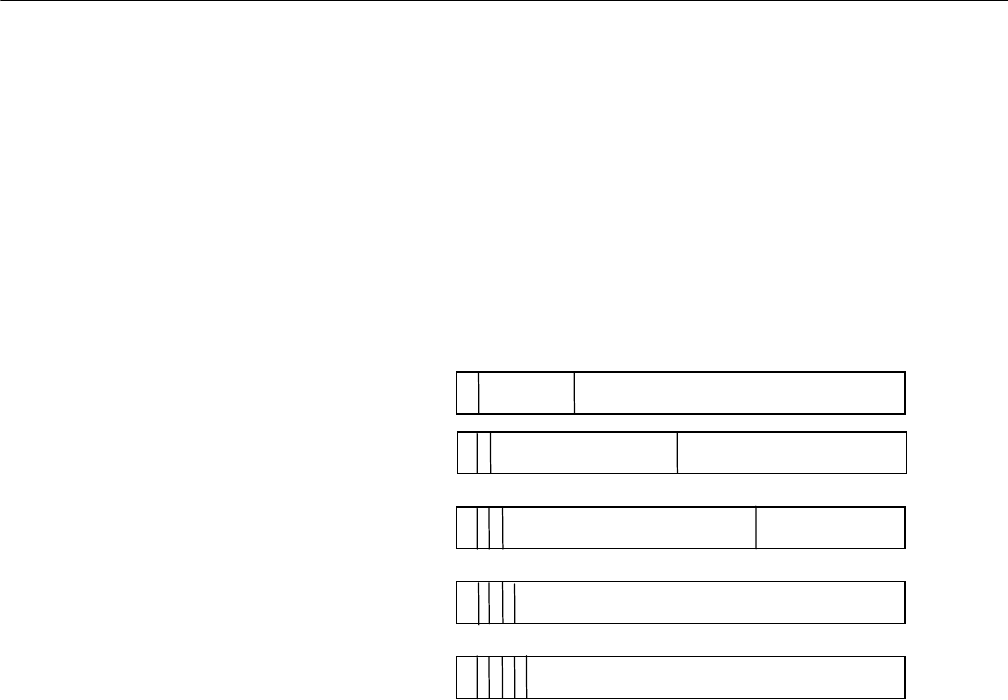
Figure 117 Classification of IP address
Address of class D is a multicast address, mainly used by IAB (Internet Architecture
Board). Address of class E is reserved for future use. At present, IP addresses are
mostly of class A, class B and class C.
When using IP addresses, it should also be noted that some of them are reserved
for special uses, and are seldom used.
0 net-id
host-id
1
host-id
110
net-id
host-id
1
110
Multicast address
1
1
1
1
0
Reserved for future use
0 1 2 3 4 8
16 24
31
Class A
Class B
Class C
Class D
Class E
net-id
—
Network number
host-id
Host number
—
net-id
0


















