Access Navigator - Release 1.8 August 2003 1-7
Introduction
SNMP
SNMP
The Access Navigator SNMP Agent is based on the SNMPv1 standard. It implements the following two
industry standard specifications for the TCP/IP and DS1 interfaces, plus an Enterprise MIB developed
for managing CA’s Access Bank II products:
l RFC 1213 – Management Information Base for Network Management of TCP/IP-based internets:
MIB-II
l RFC 1406 – Definitions of Managed Objects for the DS1 and E1 Interface Types
The Access Navigator supports:
l All mandatory objects defined in RFC 1213 for the TCP/IP network interface.
l The DS1 mandatory objects in RFC 1406 Near End Configuration Group, including the Near End
Current, Interval, and Total objects. The Far End Object Group is optional and is not currently
supported.
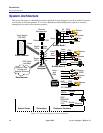
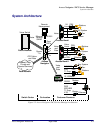
The CA Enterprise MIB provides management support for Access Navigator features not included in
the standard MIB (RFC 1213). It also enables remote management of CA products connected via the
T1 facility data link (FDL) to the Access Navigator (Figure 1-1). The CA Enterprise MIB supports:
l Access Navigator system configuration settings including SNMP
l Access Navigator interface management
l DS1 management features not supported by the standard MIB
l DS0 management
l Remote device management
l Remote crossconnect management
l Remote interface settings
l Remote DS1 settings
l Remote DS0 settings
l Remote cards and slots
The network manager can use any SNMP-compatible network management system such as
SunConnect’s SunNet Manager, HP OpenView, or Castle Rock’s SNMPc to monitor and control the
Access Navigator
The user connects to the SNMP agent through the 10Base-T Ethernet port. Before using the Ethernet
port, the user must set the IP, mask, gateway, and NMS addresses using the RS-232 command line
interface. See Provision Access Navigator on page 8-1 for instructions on how to configure these
addresses.