5-10 Intel® PXA255 Processor Developer’s Manual
DMA Controller
5.1.8 Trailing Bytes
The DMA normally transfers bytes equal to the transaction size specified by DCMD[SIZE]. As the
descriptor nears the end its data, the number of trailing bytes in the DCMD[LENGTH] field may be
smaller than the transfer size. The DMA can transfer the exact number of trailing bytes if the
DCMD[FLOWSRC] and DCMD[FLOWTRG] bits are both 0 or if it receives a corresponding
request from a peripheral or companion chip.
Trailing bytes must be considered in the following cases:
• Memory-to-Memory Moves: The DMA transfers a number bytes equal to the smaller of
DCMD[LENGTH] or DCMD[SIZE].
• Companion-Chip Related Transfers: The companion-chip must assert the request if the DMAC
must handle the trailing bytes. If the request is asserted, the DMA transfers a number of bytes
equal to the smaller of DCMD[LENGTH] or DCMD[SIZE].
• Memory to Internal Peripheral Transfers: Most peripherals send a request for trailing bytes
during memory to internal peripheral transfers. Refer to the appropriate section in this
document for details of a peripheral’s operation. The DMA transfers bytes equal to the smaller
of DCMD[LENGTH] or DCMD[SIZE].
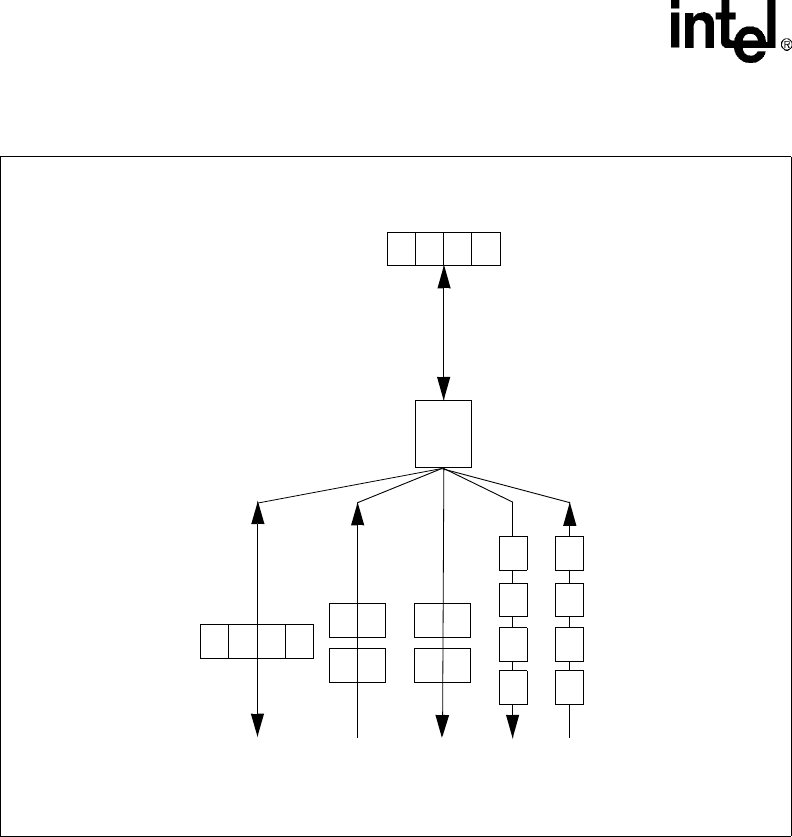
Figure 5-5. Little Endian Transfers
D[31]
D[0]
from memory
3210
DMAC
From
ToTo
From
3
2
1
03
2
1
0
1
0
10
32
32
Half-Word Wide
Device
Byte Wide
Device
Little Endian DMA Transfers
3210
To/From
Word Wide
Device


















