Intel® PXA255 Processor Developer’s Manual 9-17
I
2
C Bus Interface Unit
The I
2
C unit supports sending and receiving general call address transfers on the I
2
C bus. When
software sends a general call message from the I
2
C unit, it must set the ICR[GCD] bit to prevent
the I
2
C unit from responding as a slave. If the ICR[GCD] is not set, the I
2
C bus enters an
indeterminate state.
If the I
2
C unit acts as a slave and receives a general call address while the ICR[GCD] bit is clear, it:
• Sets the ISR[GCAD] bit
• Sets the ISR[SAD] bit
• Interrupts the processor (if the interrupt is enabled)
If the I
2
C unit receives a general call address and the ICR[GCD] bit is set, it ignores the general
call address.
Software must ensure that the I
2
C unit is not busy before it asserts a reset. Software must also
ensure that the I
2
C bus is idle when the unit is enabled after reset. When directed to reset, the I
2
C
unit, except for ISAR, returns to the default reset condition. ISAR is not affected by a reset.
When B=1, the sequence is a hardware general call and is not supported by the I
2
C unit. Refer to
the The I
2
C-Bus Specification for information on hardware general calls.
I
2
C 10-bit addresses and CBUS compatibility are not supported.
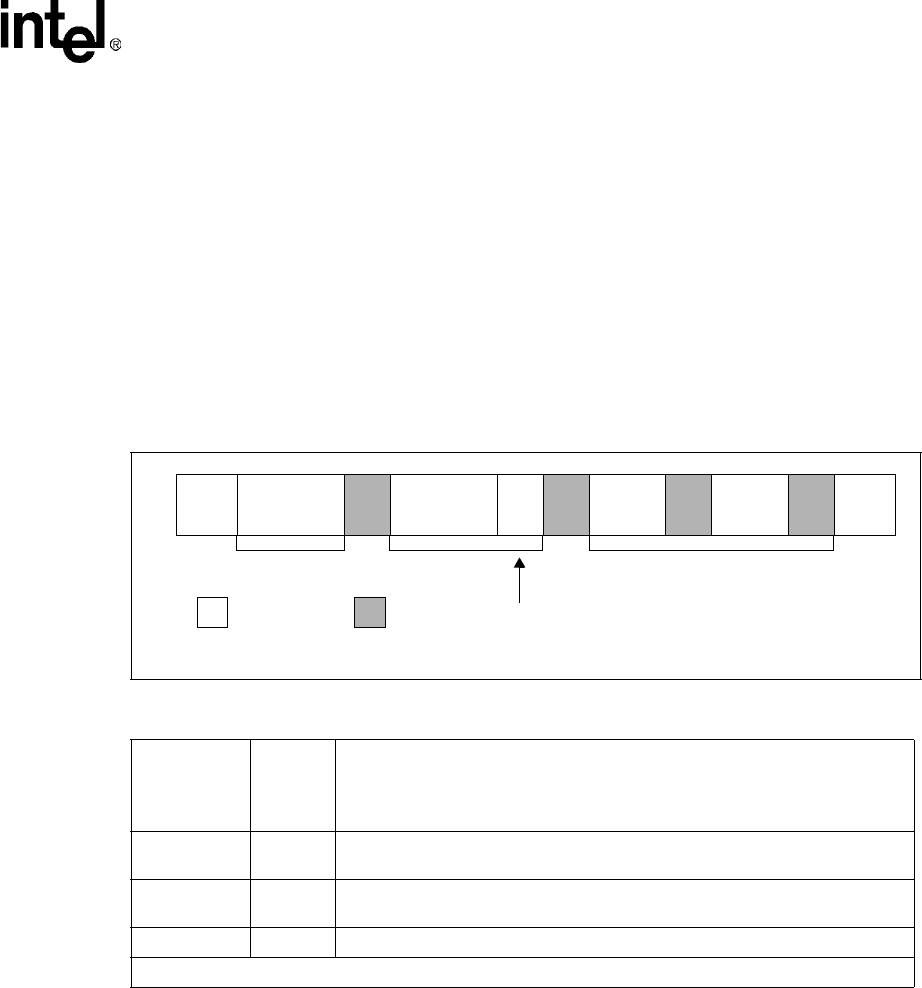
Figure 9-14. General Call Address
Table 9-7. General Call Address Second Byte Definitions
Least
Significant
Bit of Second
Byte (B)
Second
Byte
Value
Definition
00x06
2-byte transaction in which the second byte tells the slave to reset and store this
value in the programmable part of its address.
00x04
2-byte transaction in which the second byte tells the slave to store this value in
the programmable part of its address. No reset.
0 0x00 Not allowed as a second byte
NOTE: Other values are not fixed and must be ignored.
Master to Slave Slave to Master
START
00000000 ACK
Data
Byte
ACK
Data
Byte
STOP
N Bytes + ACK
Least Significant Bit of Master Address
ACK
Second Byte
Second Byte
0
ACK
First Byte
Defines Transaction


















