9-16 Intel® PXA255 Processor Developer’s Manual
I
2
C Bus Interface Unit
9.4.7 General Call Address
A general call address is a transaction with a slave address of 0x00. When a device requires the
data from a general call address, it acknowledges the transaction and stays in slave-receiver mode.
Otherwise, the device ignores the general call address. The other bytes in a general call transaction
are acknowledged by every device that uses it on the bus. Devices that do not use these bytes must
not send an ACK. The meaning of a general call address is defined in the second byte sent by the
master-transmitter. Figure 9-14 shows a general call address transaction. The least significant bit of
the second byte, called B, defines the transaction. Table 9-7 shows the valid values and definitions
when B=0.
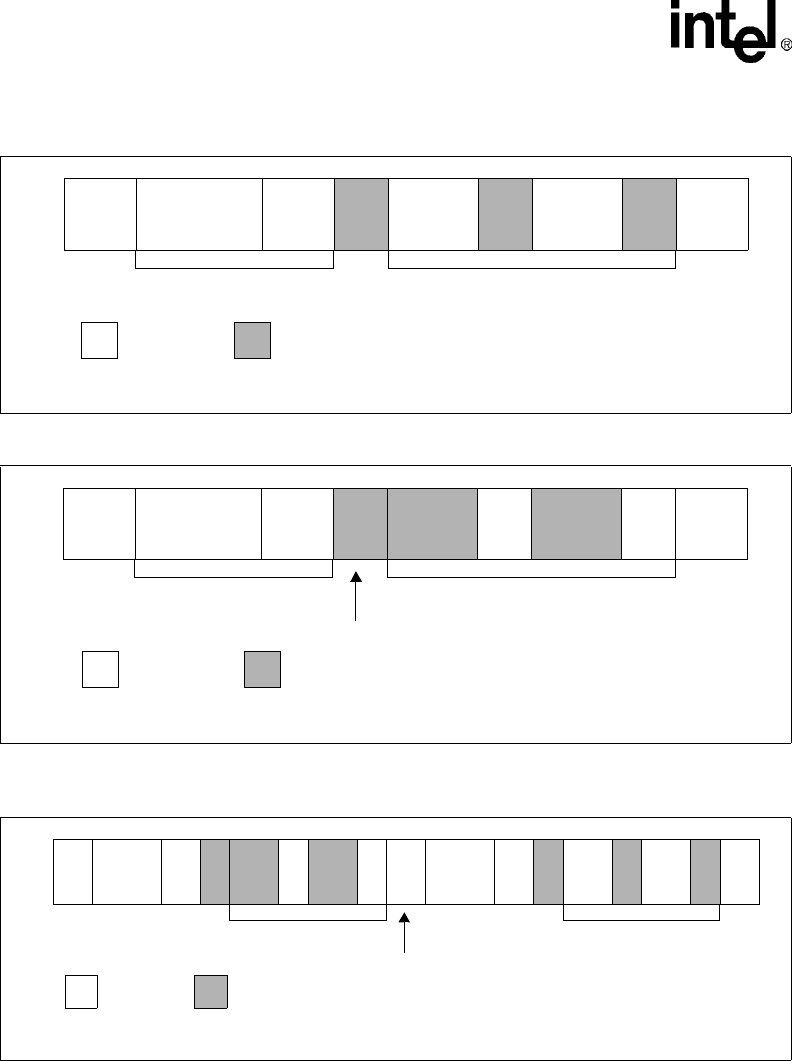
Figure 9-11. Master-Transmitter Write to Slave-Receiver
Figure 9-12. Master-Receiver Read to Slave-Transmitter
Figure 9-13. Master-Receiver Read to Slave-Transmitter, Repeated START, Master-Transmitter
Write to Slave-Receiver
Master to Slave Slave to Master
START
Slave Address
R/nW
0
ACK
Data
Byte
ACK
Data
Byte
STOP
N Bytes + ACKWrite
ACK
First Byte
Master to Slave
Slave to Master
START
Slave Address
R/nW
1
ACK
Data
Byte
ACK
Data
Byte
STOP
N Bytes + ACKRead
NAK
Default
Slave-Receive
Mode
First Byte
START
Slave
R/nW
1
ACK
Data
Byte
ACK
Data
Byte
N Bytes + ACKRead
ACK SR
Slave
R/nW
0
ACK
Data
Byte
ACK
Data
Byte
STOP
N Bytes + ACKWrite
ACK
Address Address
Master to Slave Slave to Master
Repeated
START
Data Chaining


















