9-8 Intel® PXA255 Processor Developer’s Manual
I
2
C Bus Interface Unit
9.4.2.1 Addressing a Slave Device
As a master device, the I
2
C unit must compose and send the first byte of a transaction. This byte
consists of the slave address for the intended device and a R/nW bit for transaction definition. The
MSB is transmitted first. The slave address and the R/nW bit are written to the IDBR (see
Figure 9-4).
The first byte transmission must be followed by an ACK pulse from the addressed slave. When the
transaction is a write, the I
2
C unit remains in master-transmit mode and the addressed slave device
stays in slave-receive mode. When the transaction is a read, the I
2
C unit transitions to master-
receive mode immediately following the ACK and the addressed slave device transitions to slave-
transmit mode. When a NAK is returned, the I
2
C unit aborts the transaction by automatically
sending a STOP and setting the ISR[BED] bit.
When the I
2
C unit is enabled and idle, it remains in slave-receive mode and monitors the I
2
C bus
for a START signal. When it detects a START pulse, the I
2
C unit reads the first seven bits and
compares them to those in the ISAR and the general call address (0x00). When the bits match those
in the ISAR register, the I
2
C unit reads the eighth bit (R/nW bit) and transmits an ACK pulse. The
I
2
C unit either remains in slave-receive mode (R/nW = 0) or transitions to slave-transmit mode (R/
nW = 1). See Section 9.4.7 for actions when a general call address is detected.
9.4.3 I
2
C Acknowledge
Every I
2
C byte transfer must be accompanied by an acknowledge pulse that the master- or slave-
receiver must generate. The transmitter must release the SDA line for the receiver to transmit the
acknowledge pulse (see Figure 9-5).
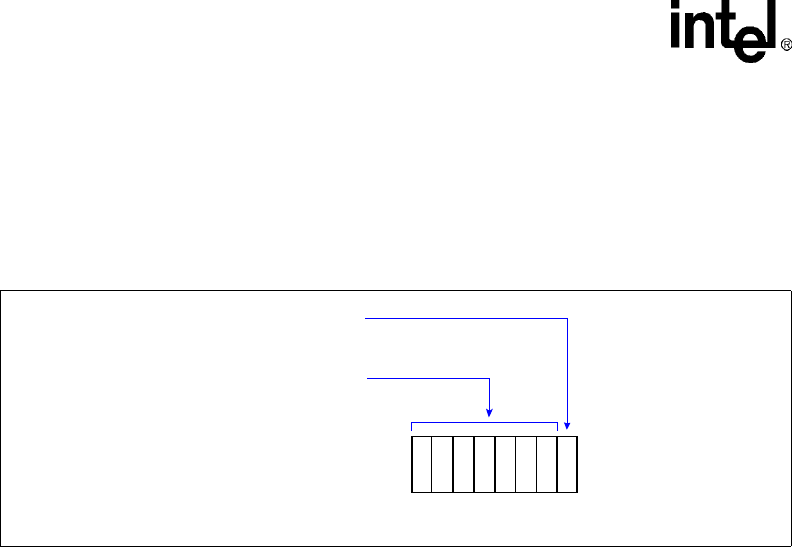
Figure 9-4. Data Format of First Byte in Master Transaction
0
7-Bit I
2
C Slave Address
7
Read/Write Transaction
MSB
LSB
(0) Write
(1) Read