Intel® PXA255 Processor Developer’s Manual 16-25
Network SSP Serial Port
Setting any of these bits also causes the corresponding status bit(s) to be set in the SSP Status
Register (SSSR). The interrupt or service request caused by the setting of one of these bits remains
active until the bit is cleared.
This is a read/write register. Ignore reads from reserved bits. Write zeros to reserved bits.
16.5.6 SSP Status Register (SSSR)
SSSR, shown in Table 16-8 contains bit fields that signal overrun errors and the transmit and
receive FIFO service requests. Each of these hardware-detected events signals an interrupt request
to the interrupt controller. The status register also contains flags that indicate:
• When the SSP is actively transmitting data
• When the transmit FIFO is not full
• When the receive FIFO is not empty
One interrupt signal is sent to the interrupt controller for each SSP. These events can cause an
interrupt:
• Receiver time-out,
• Receive FIFO overrun,
• Receive FIFO request
• Transmit FIFO request.
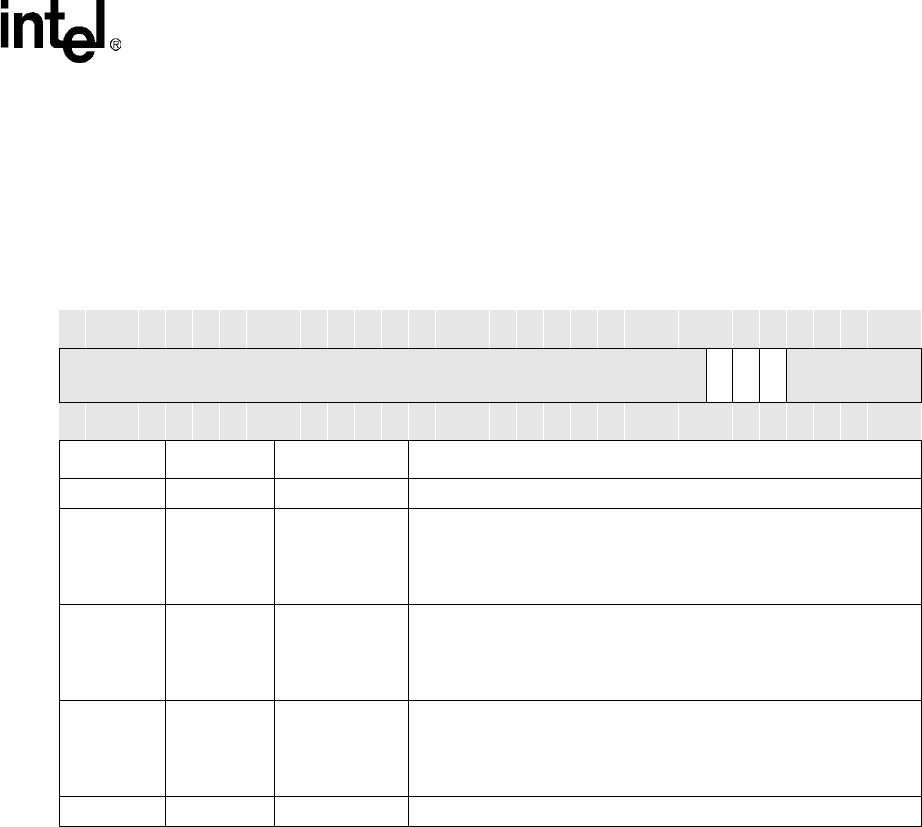
Table 16-7.
SSITR Bit Definitions
0x4140_000C SSITR Network SSP Serial Port
Bit
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
reserved
TROR
TRFS
TTFS
reserved
Reset
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 0 0 0 ? ? ? ? ?
Bits Access Name Description
31:8 — — reserved
7R/WTROR
TEST RECEIVE FIFO OVERRUN:
0 – No receive FIFO overrun service request is generated.
1 – Generates a non-maskable Interrupt to the CPU. No DMA request
is generated.
6 R/W TRFS
TEST RECEIVE FIFO SERVICE REQUEST:
0 – No receive FIFO service request is generated.
1 – Generates a non-maskable Interrupt to the CPU and a DMA
request for the receive FIFO.
5 R/W TTFS
TEST TRANSMIT FIFO SERVICE REQUEST:
0 – No transmit FIFO service request is generated.
1 – Generates a non-maskable Interrupt to the CPU and a DMA
request for the transmit FIFO.
4:0 — — reserved


















