5-8 Intel® PXA26x Processor Family Developer’s Manual
Direct Memory Access Controller
— Word [3] -> DCMDx register for the current transfer.
6. The channel waits for the request or starts the data transfer, as determined by the
DCMD[FLOW] source and target bits.
7. The channel transmits a number of bytes equal to the smaller of DCMD[SIZE] and
DCMD[LENGTH].
8. The channel waits for the next request or continues with the data transfer until the
DCMD[LENGTH] reaches zero.
9. The channel stops or continues with a new descriptor fetch from the memory, as determined by
the DDADR[STOP] bit.
Bit [0] (STOP) of Word [0] in a DMA descriptor (the low bit of the DDADRx field) marks the
descriptor at the end of a descriptor list. The value of the STOP bit does not affect the manner in
which the channel’s registers load the descriptor’s fields. If a descriptor with its STOP bit set is
loaded into a channel's registers, the channel stops after it completely transfers the data that
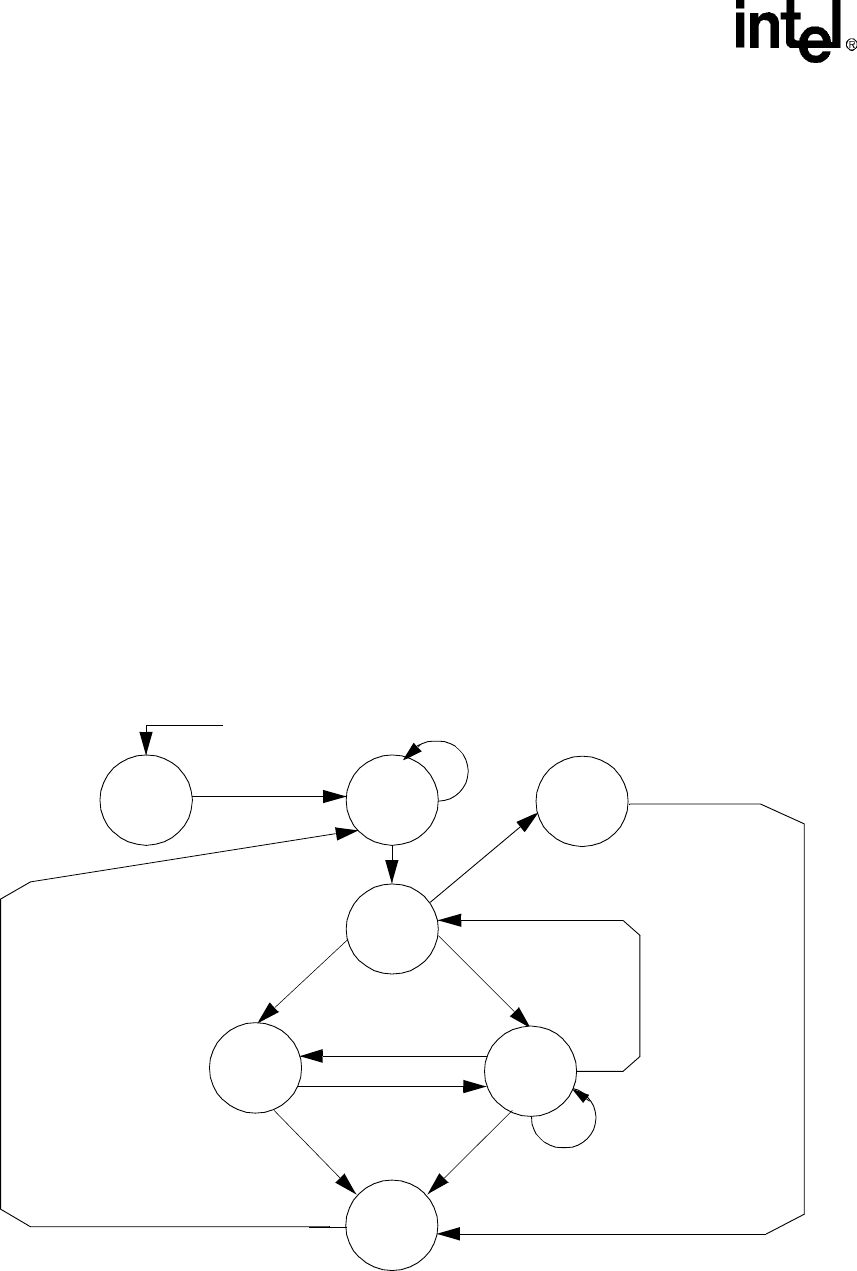
pertains to that descriptor. Figure 5-4, “Descriptor Fetch Mode Channel State” on page 5-8
summarizes this operation.
Software must set the DCSR[RUN] bit to 1 after it loads the DDADR. The channel descriptor fetch
does not take place unless the DDADR register is loaded and the DCSR[RUN] bit is set to a 1.
The DMAC priority scheme does not affect DMA descriptor fetches. The next descriptor is fetched
immediately after the previous descriptor is serviced.
Figure 5-4. Descriptor Fetch Mode Channel State
Uninitialized
Va li d
Descriptor
RESET
(Hardware or Sleep)
not running
(running)
Wait
for
request
Transferring
Data
Stopped
descriptor
fetch
Error
Channel
RUN=1
DCMD[LENGTH] 0
& DCMD[FLOWSRC] = 0
& DCMD[FLOWTRG] = 0
DDADR[STOP] = 1
DDADR[STOP] = 1
DCMD[FLOWSRC] xor
DCMD[FLOWTRG] = 1
DCMD[FLOWSRC] &
DCMD[FLOWTRG] = 0
Request Asserted
DDADR[STOP] = 0
DCMD[FLOWSRC] xor
DCMD[FLOWTRG] = 1
RUN=0
≠