8-16 Intel® PXA26x Processor Family Developer’s Manual
Synchronous Serial Port Controller
Note: Both FIFOs are cleared when the SSPC is reset or a zero is written to the SSCR0[SSE] bit.
8.7.4 SSP Status Register (SSSR)
The SSP status register (SSSR) contains bits that signal overrun errors and transmit and receive
FIFO service requests. These hardware-detected events signal an interrupt request to the interrupt
controller. The status register also contains flags that indicate when the SSP is actively transmitting
or receiving characters, when the transmit FIFO is not full, and when the receive FIFO is not empty
(no interrupt generated).
Bits that cause an interrupt signal the request as long as the bit is set. When the bit is cleared, the
interrupt is cleared. Read/write bits are called status bits, read-only bits are called flags. Status bits
are referred to as sticky (once set by hardware, they must be cleared by software). Writing a 1 to a
sticky status bit clears it. Writing a 0 has no effect. Read-only flags are set and cleared by hardware.
Writes have no effect. Some bits that cause interrupts have corresponding mask bits in the control
registers and are indicated in the section headings that follow.
Table 8-6 shows the bit locations that correspond to the status and flag bits in the SSP status
register. All bits are read-only except ROR, which is read/write. ROR’s reset state is zero. Writes to
TNF, RNE, BSY, TFS, and RFS have no effect. Writes to reserved bits are ignored and reads to
these bits are undetermined.
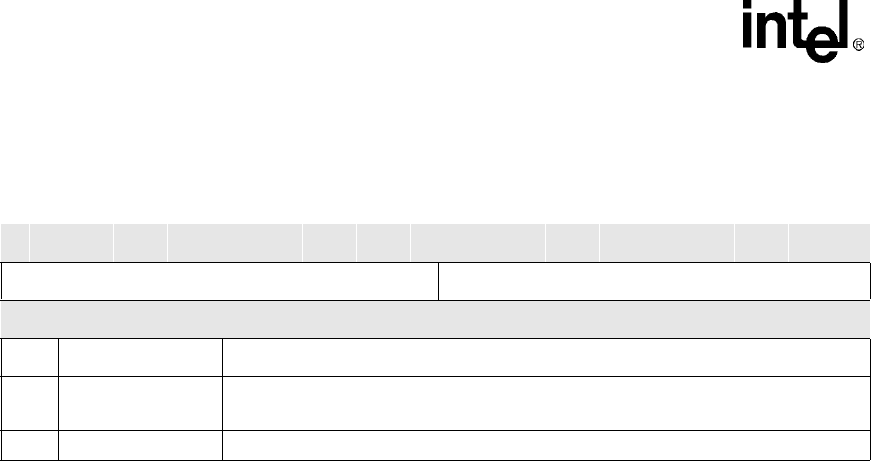
Table 8-5. SSP Data Register (SSDR) Bitmap and Definitions
0x4100 0010 SSP Data Register (SSDR)
Bit
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Reserved Transmit/Receive Data
Reset
X 0x0000
Bits Name Description
15:0
Data
DATA LOW WORD:
Data word to be written to/read from transmit/receive FIFO
31:16 — Reserved


















