Intel® PXA26x Processor Family Developer’s Manual 9-19
Inter-Integrated Circuit Bus Interface Unit
9.5.3 Read n Bytes as a Slave
To read n bytes as a slave:
1. When a slave address detected interrupt occurs.
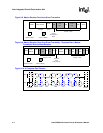
Read ISR: slave address detected (1), unit busy (1), R/nW bit (0)
2. Write a 1 to the ISR[SAD] bit to clear the interrupt.
3. Return from interrupt.
4. Set ICR[TB] bit to initiate the transfer.
5. When an IDBR receive full interrupt occurs.
Read ISR: IDBR receive full (1), ACK/NAK (0), R/nW bit (0)
6. Read IDBR to get the received byte.
7. Write a 1 to the ISR[IRF] bit to clear interrupt.
8. Return from interrupt.
9. Repeat steps 4 to 8 for n-1 times. Once the IDBR is full, the I
2
C unit will keep SCL low until
the data is read.
10. Set ICR[TB] bit to release I
2
C bus and allow next transfer.
11. When a slave stop detected interrupt occurs.
Read ISR: unit busy (0), slave STOP detected (1)
12. Write a 1 to the ISR[SSD] bit to clear interrupt.
9.6 Master Programming Examples
The following sub-sections describe master programming.
9.6.1 Initialize Unit
To initialize the unit:
1. Set the slave address in the ISAR.
2. Enable desired interrupts in the ICR. Do not enable arbitration loss detected interrupt
3. Set the ICR[IUE] and ICR[SCLE] bits to enable the I
2
C unit and SCL.
9.6.2 Write 1 Byte as a Master
To write 1 byte as a master:
1. Load target slave address and R/nW bit in the IDBR. R/nW must be 0 for a write.
2. Initiate the write.
Set ICR[START], clear ICR[STOP], clear ICR[ALDIE], set ICR[TB]
3. When an IDBR transmit empty interrupt occurs.
Read ISR: IDBR transmit empty (1), unit busy (1), R/nW bit (0)
4. Write a 1 to the ISR[ITE] bit to clear interrupt.