7-2 Intel® PXA26x Processor Family Developer’s Manual
Liquid Crystal Display Controller
from the dither logic is grouped into the selected format (e.g., 8-bit color, dual panel, 16-bit color.,
etc.) and placed in a FIFO buffer before being sent out on the LCD controller’s pins and driven to
the display using the pixel clock.
Depending on the type of panel used, the LCD controller is programmed to use either 4-, 8-, or 16-
pixel data output pins. Single-panel monochrome displays use either four or eight data pins to send
4 or 8 pixels for each pixel clock. Single-panel color displays use eight pins to send 2-2/3 pixels
each pixel clock (8 pins / 3 colors/pixel = 2 2/3 pixels per clock). The LCD controller also supports
dual-panel mode, in which the LCD controller’s data lines are split into two groups, one to drive
the top half and one to drive the bottom half of the screen. For dual-panel displays, the number of
pixel data output pins is doubled, allowing twice as many pixels to be sent each pixel clock to the
two halves of the screen.
In active-color-display mode, the LCD controller can drive TFT displays. When using 1-, 2-, 4-, or
8-bit modes, the LCD’s dither logic is bypassed, and the pixel value is sent from the palette buffer
directly to the LCD’s data output pins. 16-bit pixel mode bypasses both the palette and the dither
logic.
7.1.1 Features
The processor LCD controller supports these features:
• Display modes:
— Single- or dual-panel displays
— Up to 256 gray-scale levels (8 bits) in passive monochrome mode
— A total of 65536 possible colors in passive color mode (using the 16-bit TMED dithering
algorithm)
— Up to 65536 colors in active color mode (16 bits, bypasses palette)
— Passive 8-bit color single-panel displays
— Passive 8-bit (per panel) color dual-panel displays
• Display sizes up to 1024x1024 pixels, recommended maximum of 640x480x16 for 32 bit
SDRAM bus and 320x240x16 for 16 bit SDRAM bus
• Internal color palette RAM 256 entry by 16 bits (can be loaded automatically at the beginning
of each frame)
• Encoded pixel data of 1, 2, 4, 8, or 16 bits
• Programmable toggle of AC bias pin output (toggled by line count)
• Programmable pixel clock from 195 KHz to 83 MHz (100 MHz/512 to 166 MHz/2)
• Integrated 2-channel DMA (one channel for palette and single panel, the other channel for
second panel in dual-panel mode).
• Programmable wait-state insertion at the beginning and end of each line
• Programmable polarity for output enable, frame clock, and line clock
• Programmable interrupts for input and output FIFO underrun
• Programmable frame and line clock polarity, pulse width, and wait counts
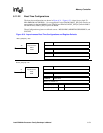
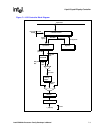
Figure 7-1 illustrates a simplified, top-level block diagram for the processor LCD controller.