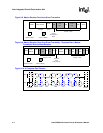
Intel® PXA26x Processor Family Developer’s Manual 9-13
Inter-Integrated Circuit Bus Interface Unit
When the CPU needs to read data, the I
2
C unit transitions from slave-receive mode to master-
transmit mode to transmit the start address, R/nW bit, and the ACK pulse. After it sends the ACK
pulse, the I
2
C unit transitions to master-receive mode and waits to receive the read data from the
slave device (see Figure 9-8 on page 9-14).Multiple transactions can take place during an I
2
C
operation. For example, transitioning from master-receive to master-transmit through a repeated
start.
Read one byte
of I
2
C Data
from the IDBR
Master-receive
only
I
2
C master operation data receive mode.
Eight bits are read from the serial bus, collected in the shift register then
transferred to the IDBR after the ICR[ACKNAK] bit is read.
The CPU reads the IDBR when the ISR[IRF] bit is set and the ICR[TB] bit
is clear. If IDBR Receive Full Interrupt is enabled, it is signalled to the
CPU.
When the IDBR is read, if the ISR[ACKNAK] is clear (indicating ACK),
the processor writes the ICR[ACKNAK] bit and set the ICR[TB] bit to
initiate the next byte read.
If the ISR[ACKNAK] bit is set (indicating NAK), ICR[TB] bit is clear,
ICR[STOP] bit is set, and ISR[UB] bit is set, then the last data byte has
been read into the IDBR and the I
2
C unit is sending the STOP.
If the ISR[ACKNAK] bit is set (indicating NAK), ICR[TB] bit is clear, but
the ICR[STOP] bit is clear, then the CPU has two options: 1. set the
ICR[START] bit, write a new target address to the IDBR, and set the
ICR[TB] bit which will send a repeated start condition or 2. set the
ICR[MA] bit and leave the ICR[TB] bit clear which will send a STOP only.
Transmit
Acknowledge
to slave-
transmitter
Master-receive
only
As a master-receiver, the I
2
C unit generates the clock for the
acknowledge pulse. The I
2
C unit is also responsible for driving the SDA
line during the ACK cycle.
If the next data byte is to be the last transaction, the CPU will set the
ICR[ACKNAK] bit for NAK generation.
See Section 9.4.3, “Inter-Integrated Circuit Acknowledge”.
Generate a
Repeated
START to
chain I
2
C
transactions
Master-transmit
Master-receive
If data chaining is desired, a repeated START condition is used instead
of a STOP condition.
This occurs after the last data byte of a transaction has been written to
the bus.
The CPU will write the next target slave address and the R/nW bit to the
IDBR, set the ICR[START] bit, and set the ICR[TB] bit.
See Section 9.3.3, “Start and Stop Bus States”.
Generate a
STOP
Master-transmit
Master-receive
Generated after the CPU writes the last data byte on the bus.
CPU
generates a STOP condition by setting the ICR[STOP] bit.
See Section 9.3.3, “Start and Stop Bus States”.
Table 9-5. Master Transactions (Sheet 2 of 2)
I
2
C Master
Action
Mode of
Operation
Definition