Figure
6-68.
pgBlQ6-c
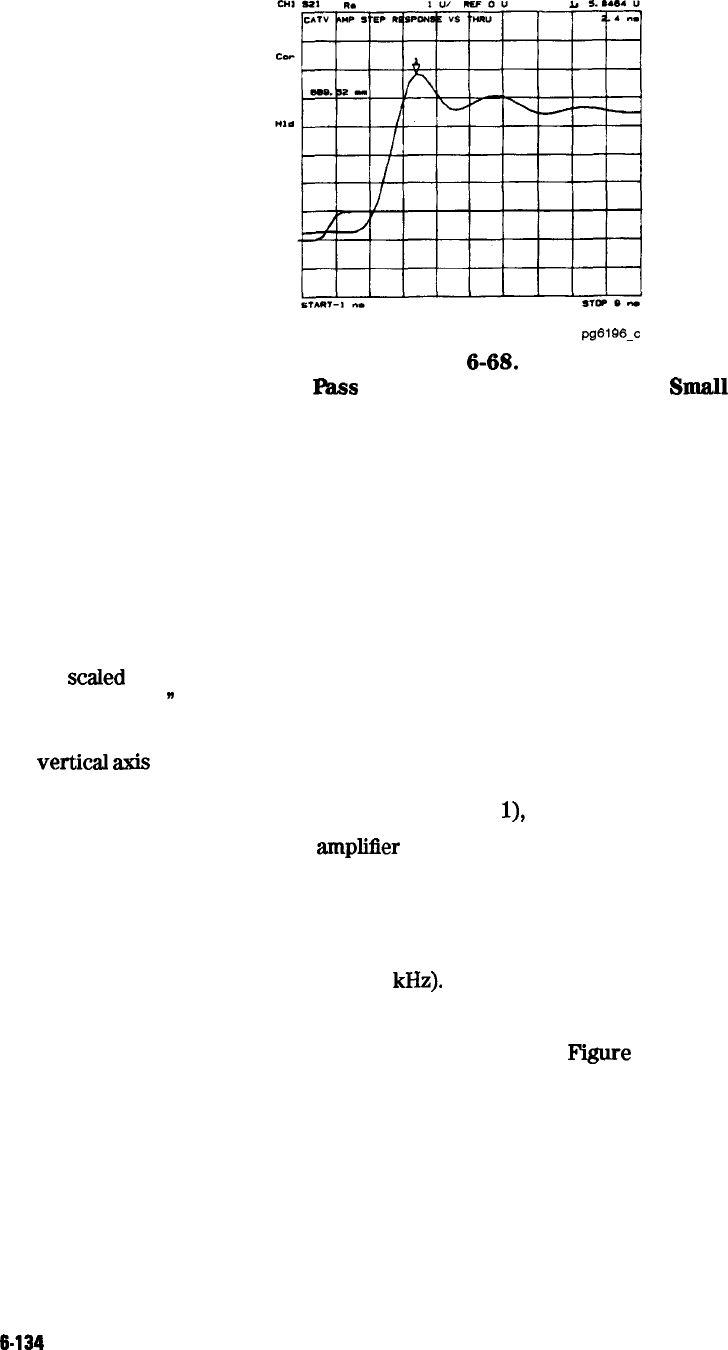
Time Domain Low Pass Measurement of an Amplifier Small Signal
Transient Response
Interpreting the low pass step transmission response horizontal axis. The low pass
transmission measurement horizontal axis displays the average transit time through the
test device over the frequency range used in the measurement. The response of the thru
connection used in the calibration is a step that reaches 50% unit height at approximately
time = 0. The rise time is determined by the highest frequency used in the frequency domain
measurement. The step is a unit high step, which indicates no loss for the thru calibration.
When a device is inserted, the time axis indicates the propagation delay or electrical length
of the device. The markers read the electrical delay in both time and distance. The distance
can be
scaled
by an appropriate velocity factor as described earlier in this section under “Time
domain bandpass.
n
Interpreting the low pass step transmission response vertical
axis. In the real format,
the
vertical
azis
displays the transmission response in real units (for example, volts). For the
amplifier example in Figure 6-68, if the amplifier input is a step of 1 volt, the output,
2.4 nanoseconds after the step (indicated by marker
l),
is 5.84 volts.
In the log magnitude format, the
ampliher
gain is the steady state value displayed after the
initial transients die out.
Measuring separate transmission paths through the test device using low pass impulse
mode.
The low pass impulse mode can be used to identify different transmission paths through
a test device that has a response at frequencies down to dc (or at least has a predictable
response, above the noise floor, below 30
kHz).
For example, use the low pass impulse mode to
measure the relative transmission times through a multi-path device such as a power divider.
Another example is to measure the pulse dispersion through a broadband transmission line,
such as a fiber optic cable. Both examples are illustrated in
F’igure
6-69. The horizontal and
vertical axes can be interpreted as already described in this section under “Time Domain
Bandpass”,
6-134
Application and Operation Concepts


















