SUBB
Subtract From Accumulator With Borrow
7-178
Syntax SUBB
dma
Direct addressing
SUBB
ind
[, AR
n
] Indirect addressing
Operands dma: 7 LSBs of the data-memory address
n: Value from 0 to 7 designating the next auxiliary register
ind: Select one of the following seven options:
* *+ *– *0+ *0– *BR0+ *BR0–
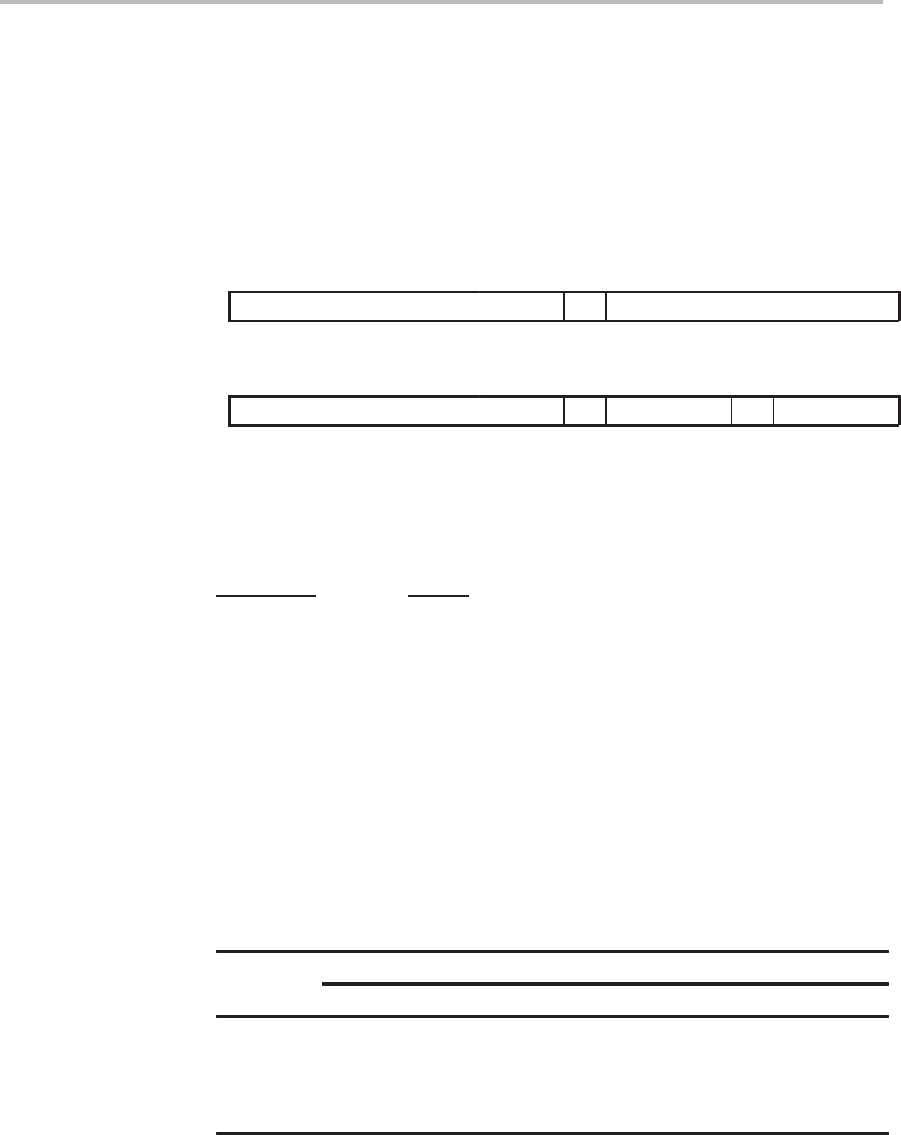
SUBB
dma
1514131211109876543210
0
11001000 dma
SUBB
ind
[, AR
n
]
1514131211109876543210
0
11001001 ARU N NAR
Note: ARU, N, and NAR are defined in Section 6.3,
Indirect Addressing Mode
(page 6-9).
Execution Increment PC, then ...
(ACC) – (data-memory address) – (logical inversion of C) → ACC
Status Bits
Affected by Affects
OVM OV and C
This instruction is not affected by SXM.
Description The content of the addressed data-memory location and the logical inversion
of the carry bit is subtracted from the accumulator with sign extension sup-
pressed. The carry bit is then affected in the normal manner: the carry bit is
cleared (C = 0) if the result of the subtraction generates a borrow and is set
(C = 1) if it does not generate a borrow.
The SUBB instruction can be used in performing multiple-precision arithmetic.
Words 1
Cycles for a Single SUBB Instruction
Program
Operand ROM DARAM SARAM External
DARAM 1 1 1 1+p
SARAM 1 1 1, 2
†
1+p
External 1+d 1+d 1+d 2+d+p
†
If the operand and the code are in the same SARAM block
Opcode
Cycles


















