Device-Specific Information
4-32
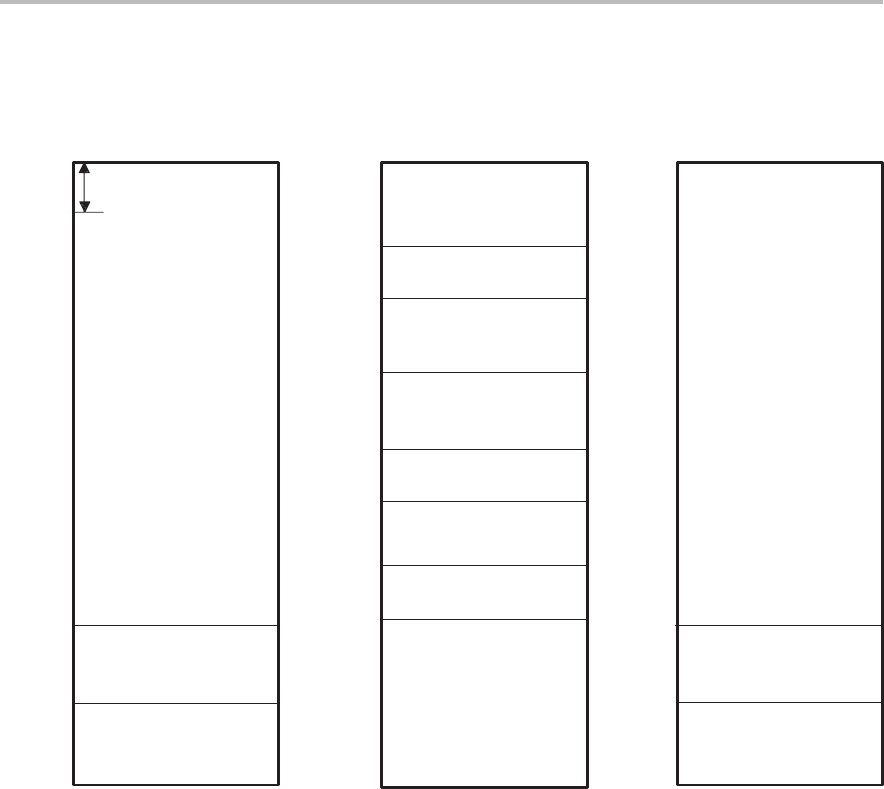
Figure 4–16. ’C203 Address Map
FFFFh
’C203 Program ’C203 Data
FFFFh
0800h
0400h
03FFh
0300h
02FFh
0200h
01FFh
0080h
007Fh
0060h
005Fh
0000h
External
DARAM B1
§
On-chip
Reserved (CNF = 1)
B0
‡
(CNF = 0);
On-chip DARAM
Reserved
DARAM B2
On-chip
reserved addresses
registers and
Memory-mapped
0000h
FDFFh
FE00h
External (CNF = 0)
Reserved (CNF = 1);
External
FEFFh
FF00h
FFFFh
On-chip DARAM
B0
†
(CNF = 1);
External (CNF = 0)
Reserved
07FFh
003Fh
Interrupts (external)
’C203 I/O
0000h
External
reserved addresses
registers and
I/O-mapped
External
(local and/or global)
FF00h
FEFFh
FF10h
FF0Fh
Reserved for
test/emulation
8000h
7FFFh
†
When CNF = 1, addresses FE00h–FEFFh and FF00h–FFFFh are mapped to the same physical block (B0) in program-memory
space. For example, a write to FE00h will have the same effect as a write to FF00h. For simplicity, addresses FE00h–FEFFh
are referred to here as reserved when CNF = 1.
‡
When CNF = 0, addresses 0100h–01FFh and 0200h–02FFh are mapped to the same physical block (B0) in data-memory
space. For example, a write to 0100h will have the same effect as a write to 0200h. For simplicity, addresses 0100h–01FFh are
referred to here as reserved.
§
Addresses 0300h–03FFh and 0400h–04FFh are mapped to the same physical block (B1) in data-memory space. For example,
a write to 0400h has the same effect as a write to 0300h. For simplicity, addresses 0400h–04FFh are referred to here as
reserved.