SUBC
Conditional Subtract
7-180
Syntax SUBC
dma
Direct addressing
SUBC
ind
[, AR
n
] Indirect addressing
Operands dma: 7 LSBs of the data-memory address
n: Value from 0 to 7 designating the next auxiliary register
ind: Select one of the following seven options:
* *+ *– *0+ *0– *BR0+ *BR0–
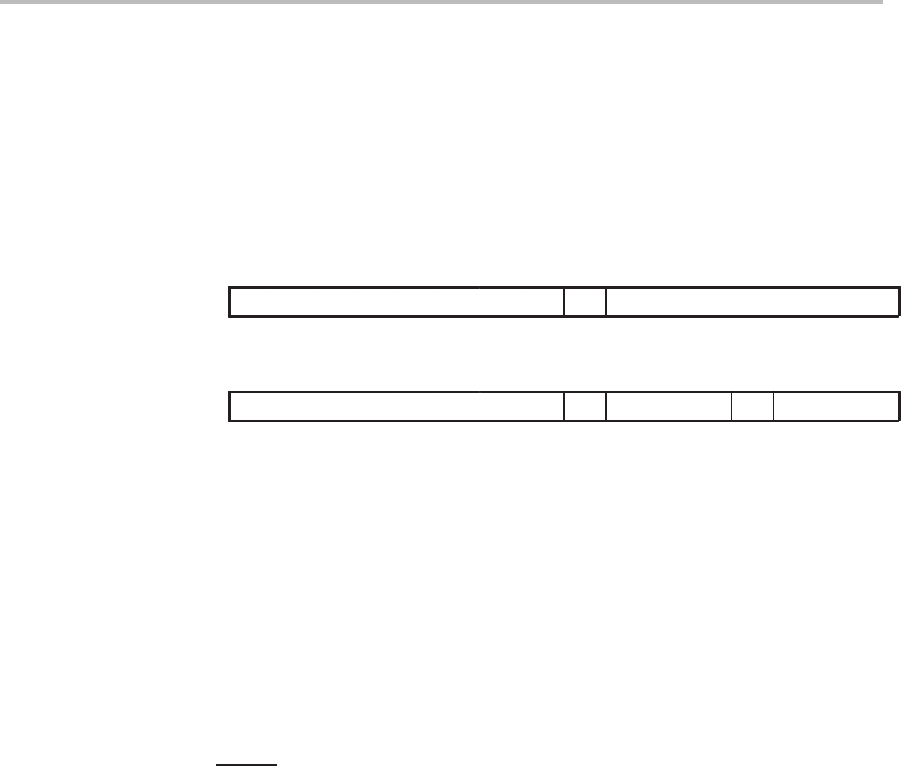
SUBC
dma
1514131211109876543210
0
00010100 dma
SUBC
ind
[, AR
n
]
1514131211109876543210
0
00010101 ARU N NAR
Note: ARU, N, and NAR are defined in Section 6.3,
Indirect Addressing Mode
(page 6-9).
Execution For (ACC) ≥ 0 and (data-memory address) ≥ 0:
Increment PC, then ...
(ACC) – [(data-memory address) × 2
15
] → ALU output
If ALU output ≥ 0
Then (ALU output) × 2 + 1 → ACC
Else (ACC) × 2 → ACC
Status Bits
Affects
OV and C
Description The SUBC instruction performs conditional subtraction, which can be used for
division as follows: Place a positive 16-bit dividend in the low accumulator and
clear the high accumulator. Place a 16-bit positive divisor in data memory.
Execute SUBC 16 times. After completion of the last SUBC, the quotient of the
division is in the lower-order 16 bits of the accumulator, and the remainder is
in the higher-order 16 bits of the accumulator. For negative accumulator and/or
data-memory values, SUBC cannot be used for division.
If the 16-bit dividend contains fewer than 16 significant bits, the dividend may
be placed in the accumulator and left shifted by the number of leading nonsig-
nificant 0s. The number of executions of SUBC is reduced from 16 by that num-
ber. One leading 0 is always significant.
SUBC operations performed as stated above are not affected by the sign-ex-
tension mode bit (SXM).
Opcode


















