1100 | VLAN
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Virtual LANs (VLANs) are a cost-effective method of segmenting and organizing a network. A single
switch can be divided into multiple broadcast domains so that devices can be grouped and isolated; each
logical segment is virtual LAN. Applying VLANs reduces broadcast traffic, introduces flexibility in the
placement of devices on the network, and increases network security by allowing separate policies to be
applied to each group.
Port-based VLANs
On FTOS, a VLAN is a user-defined group of ports (there is also the concept of protocol-based VLANs).
Ports in different VLANs do not communicate unless routing is configured between them. A port may
belong to more than one VLAN. Typically, ports connected to a host belong to only one VLAN, and ports
on an inter-switch link belong to more than one VLAN; these ports are sometimes called trunk ports.
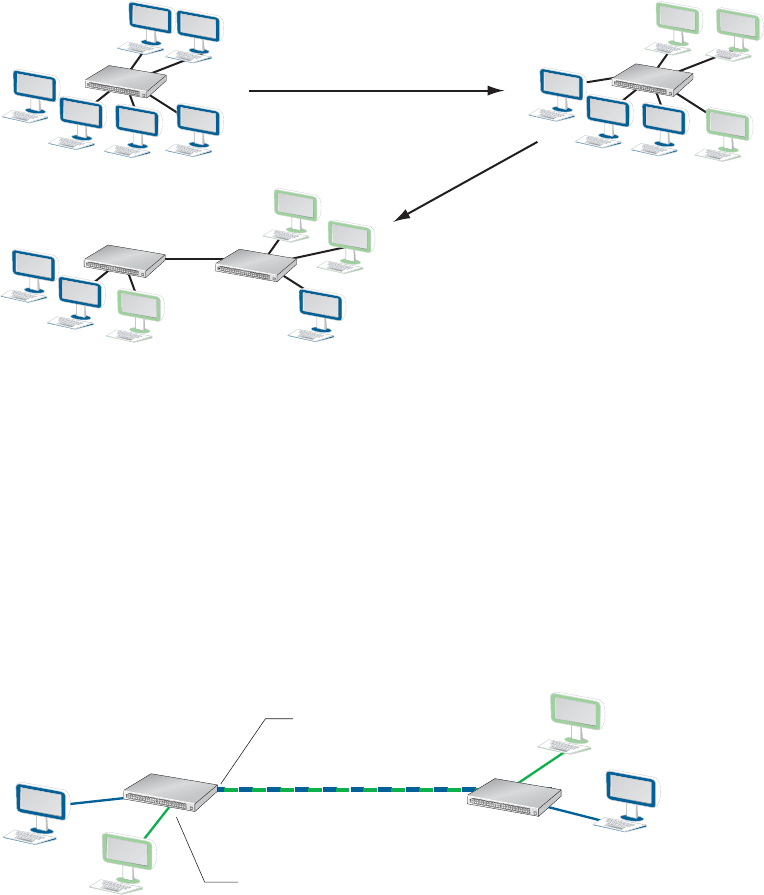
Figure 56-1. VLAN Membership
VLANs can logically organize users
into groups increasing performance
Users on VLANs are not constrained
to a physical location
On a LAN users are bound to a physical location
and performance is reduced with a large number of users
Ports of an inter-switch
link typically belong to
multiple VLANs
VLAN 100
VLAN 200
Ports connected to end-stations
typically belong to a single VLAN


















