IPv6 Addressing | 493
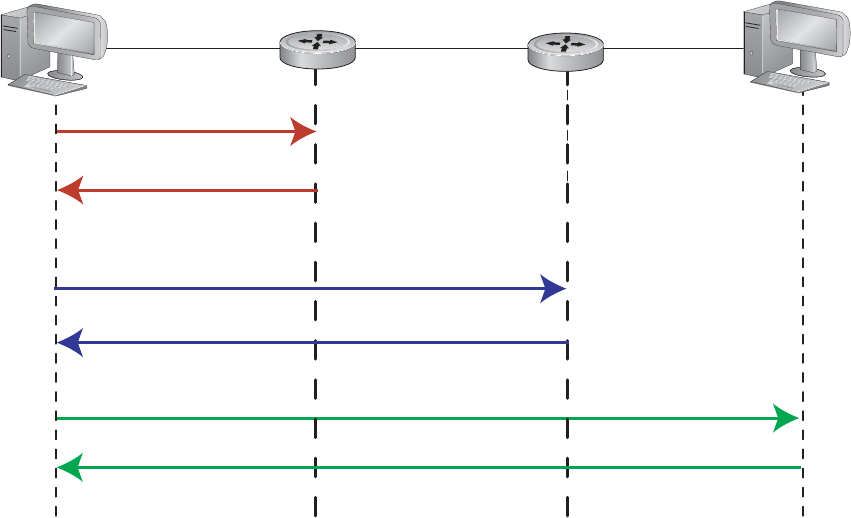
Path MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) defines the largest packet size that can traverse a
transmission path without suffering fragmentation.
Path MTU for IPv6 uses ICMPv6 Type-2
messages to discover the largest MTU along the path from source to destination and avoid the need to
fragment the packet.
The recommended MTU for IPv6 is 1280. Greater MTU settings increase processing efficiency because
each packet carries more data while protocol overheads (headers, for example) or underlying per-packet
delays remain fixed.
Figure 22-2. MTU Discovery Path
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
IPv6 NDP is supported on platforms c e s
Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is a top-level protocol for neighbor discovery on an IPv6 network. In
lieu of ARP, NDP uses "Neighbor Solicitation" and "Neighbor Advertisement" ICMPv6 messages for
determining relationships between neighboring nodes. Using these messages, an IPv6 device learns the
link-layer addresses for neighbors known to reside on attached links, quickly purging cached values that
become invalid.
With ARP, each node broadcasts ARP requests on the entire link. This approach causes unnecessary
processing by uninterested nodes. With NDP, each node sends a request only to the intended destination
via a multicast address with the unicast address used as the last 24 bits. Other hosts on the link do not
participate in the process, greatly increasing network bandwidth efficiency.
Router B
Router A
MTU = 1600 MTU =
1400 MTU = 1200
ICMPv6 (Type 2)
Use MTU = 1400
Packet (MTU = 1600)
Packet (MTU = 1400)
ICMPv6 (Type 2
)
Use MTU = 1200
Packet (MTU = 1200)
Packet Received
Source
Destination


















