Private VLANs | 831
39
Private VLANs
Private VLANs is available on platforms: c s
Private VLANs (PVLANs) provide Layer 2 isolation between ports within the same VLAN. That is,
peer-to-peer communication is restricted or blocked. This is done by dividing the VLAN, into subdomains,
and then restricting or blocking traffic flow between them.
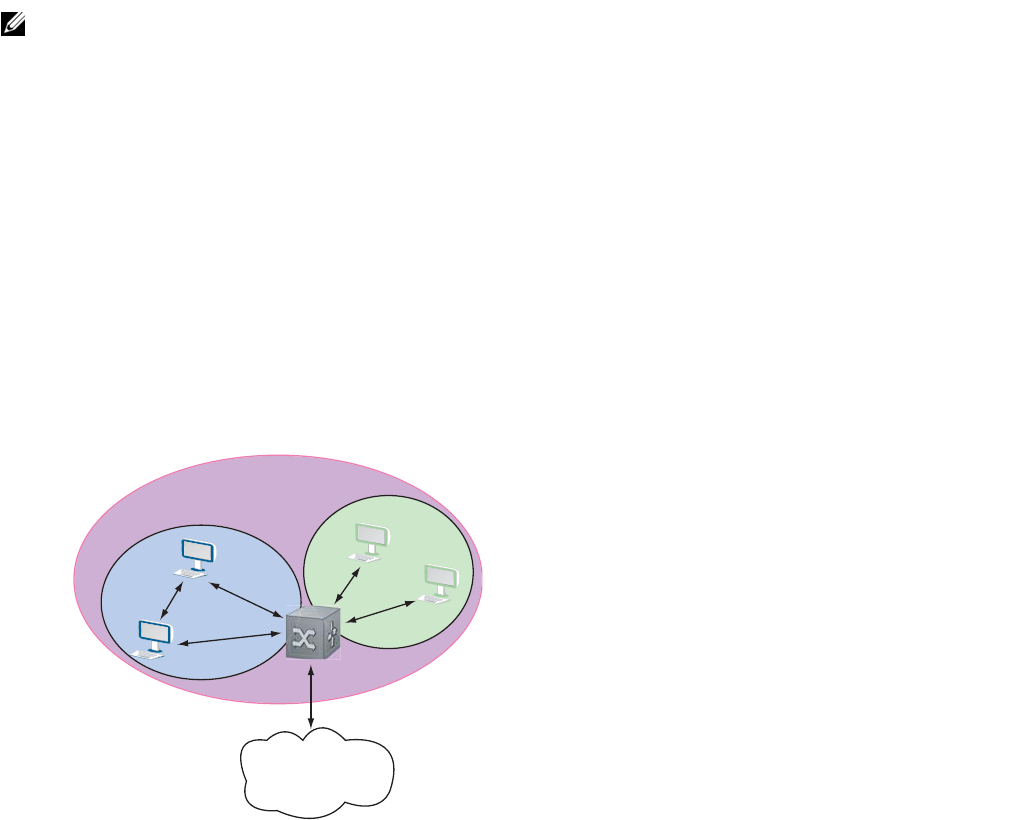
The VLAN that is divided into subdomains is called the Primary VLAN; the subdomains are called
secondary VLANs. There are two types of secondary VLANs:
• Community VLAN — a group of ports in which ports may communicate with each other and
promiscuous ports, but not to ports outside of their own secondary VLAN. A service provider can
provide Layer 2 security for customers and use the IP addresses more efficiently, by using a separate
community VLAN per customer, while at the same time using the same IP subnet address space for all
community and isolated VLANs mapped to the same primary VLAN.
• Isolated VLAN — a group of ports in which ports may communicate with promiscuous ports only;
they may not communicate with each other, or to other ports outside of their own secondary VLAN.
An enterprise, such as a hotel, can use an isolated VLAN in a private VLAN to provide Internet access
for its guests, while stopping direct access between the guest ports.
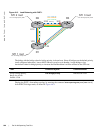
Figure 39-1. PVLAN: Primary and Secondary VLANs
Note: While conceptually, the primary VLAN is divided into secondary VLANs, when configuring PVLAN
in FTOS, you explicitly define the secondary VLANs, and then make them members of the primary VLAN.
Primary VLAN
Community
VLAN
Isolated
VLAN
Network