614 | Multicast Listener Discovery
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
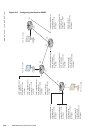
Figure 27-4. Port Inheritance on Mixed-mode VLANs
In Figure 27-4, the host on Port 1 sends an exclude—that is, exclude nothing—report to join group G and
receive traffic from all transmitting sources for the group. FTOS creates a (*,G) entry and lists Port 1 in the
outgoing interface list. The host on Port 3 sends an include report to join the same group G, but receive
traffic from only source S. FTOS creates a (S,G) entry and could list Port 3 as the outgoing interface.
However, inbound traffic matches against the most specific entry, in this case, traffic from source S for
group G matches the (S,G) entry. So, this traffic is forwarded out of only Port 3, which means that Port 1,
which requested traffic from all sources, would be denied (S,G) traffic.
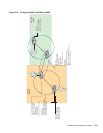
To reconcile this behavior, FTOS adds (*,G) ports to (S, G) entries. These inherited ports are marked with
an asterisk to differentiate them from ports that have been snooped. In Figure 27-4, the (S,G) entry inherits
Port 1 from the (*,G) entry. Now, (S,G) traffic is forwarded out Ports 1 and 3, so that Port 1 receives traffic
from all sources, as requested.
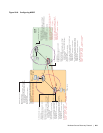
Note: IGMPv3 does not inherit ports like MLDv2. Instead, when a VLAN has hosts that want to include
and exclude the same source, S, the group defaults to exclude mode. That is, no (S,G) entry installed,
and the excluding host receives all traffic. Notice, that in Figure 27-4, the MLD snooping table has an
(S,G) entry, while the IGMP snooping does not.
VLAN 10
1
2
3
4
include (S,G)
exclude (*,G)
(*,G)
1
(S,G)
1*, 3
Snooping Table
MLDv2
IGMP
(*,G)
1, 3