1106 | VLAN
www.dell.com | support.dell.com
Figure 56-5. Communicating between VLANs
Use a Native VLAN on Trunk Ports
Traditionally, a port may either be an untagged member of a single VLAN or a tagged member of multiple
VLANs. However, FTOS allows you to make a port an untagged member and a tagged member of
VLANs, concurrently.
Ports that are an untagged and tagged member concurrently are called hybrid ports; physical ports and
port-channels may be hybrid ports. On a hybrid port, the VLAN of which the port is an untagged member
is the native VLAN.
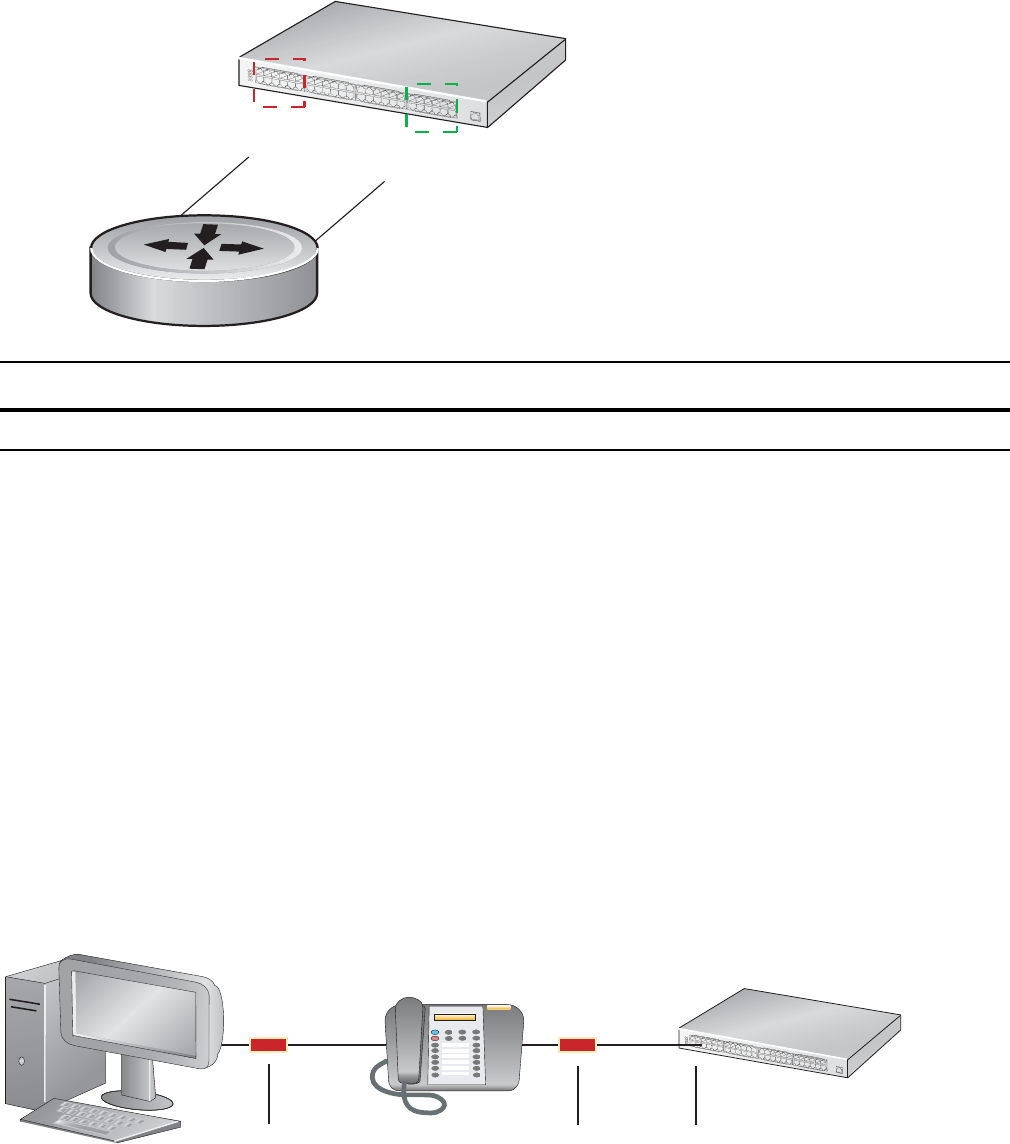
A Native VLAN is useful on trunk ports, which receive both tagged and untagged traffic (a trunk port is a
port that carries traffic for one or more VLANs on the switch). The classic example is a VOIP phone and a
PC connected to the same port of a switch, where the VOIP phone generates packets tagged with VLAN
ID = VOICE VLAN, and the PC generates untagged packets.
Figure 56-6. Using Native VLANs with PC/VOIP Phone
Task Command Syntax Command Mode
Assign an IP address to a VLAN interface. ip address address/mask INTERFACE VLAN
VLAN 100
10.11.100.1/24
VLAN 200
10.11.200.1/24
untagged member of VLAN 100 (native)
tagged member of VLAN 200
untagged
tagged VLAN 200


















