Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) | 1127
58
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP)
IPv4 Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is available on platforms: c e s
IPv6 VRRP (VRRP version 3) is available on platforms: c e s
This chapter covers the following information:
• VRRP Overview
• VRRP Benefits
• VRRP Implementation
• VRRP Configuration
• Sample Configurations
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is designed to eliminate a single point of failure in a
statically routed network.
VRRP Overview
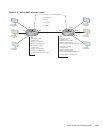
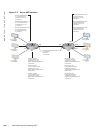
VRRP specifies a MASTER router that owns the next hop IP and MAC address for end stations on a LAN.
The MASTER router is chosen from the virtual routers by an election process and forwards packets sent to
the next hop IP address. If the MASTER router fails, VRRP begins the election process to choose a new
MASTER router and that new MASTER continues routing traffic.
VRRP uses the Virtual Router Identifier (VRID) to identify each virtual router configured The IP address
of the MASTER router is used as the next hop address for all end stations on the LAN. The other routers
represented by IP addresses are BACKUP routers.
VRRP packets are transmitted with the virtual router MAC address as the source MAC address. The MAC
address is in the following format: 00-00-5E-00-01-{VRID}. The first three octets are unchangeable. The
next two octets (00-01) indicate the address block assigned to the VRRP protocol, and are unchangeable.
The final octet changes depending on the VRRP Virtual Router Identifier and allows for up to 255 VRRP
routers on a network.