©2008 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
LPC ISA Bridge (Device 20, Function 3)
AMD SB600 Register Reference Manual Proprietary Page 260
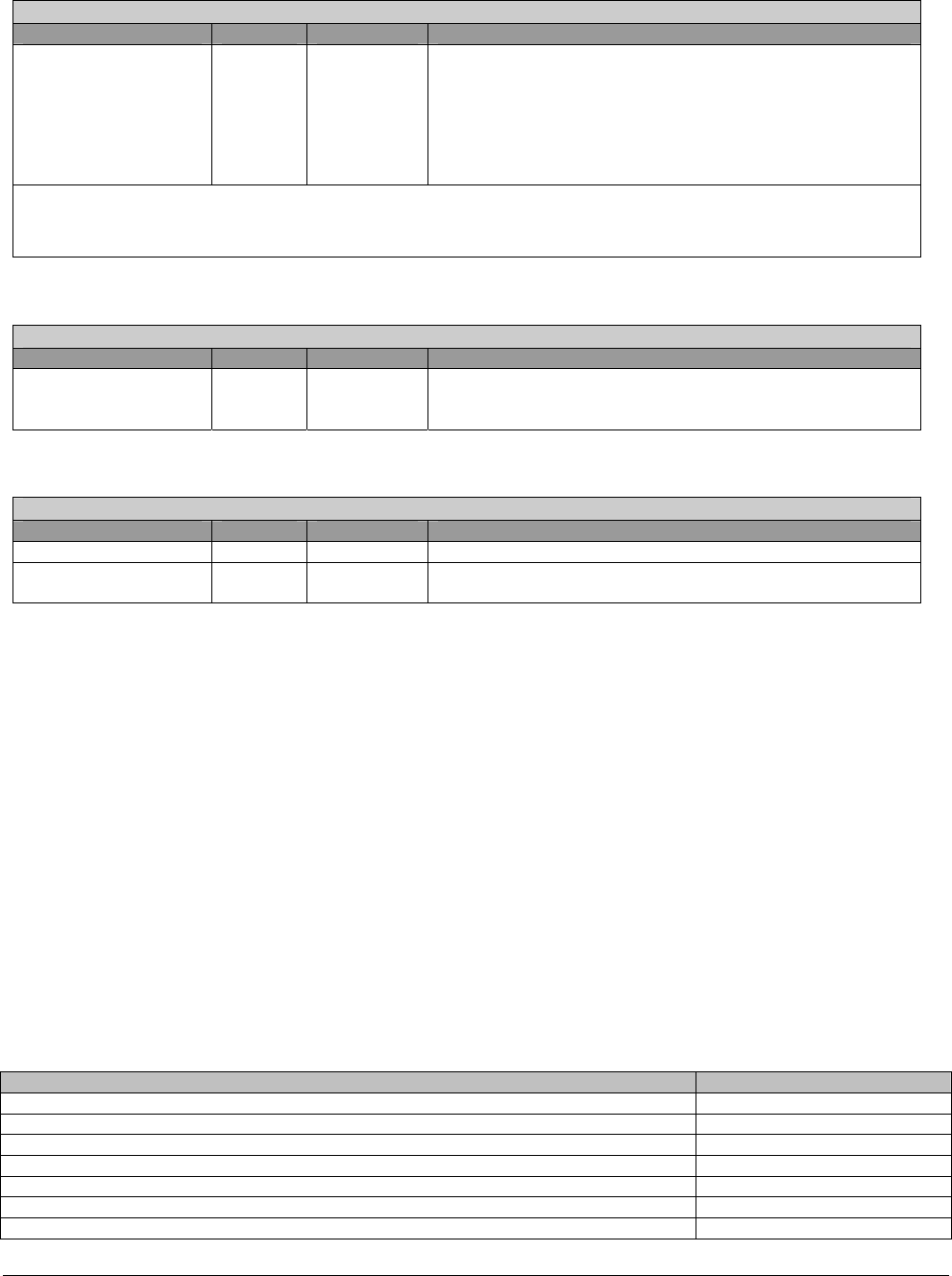
TMKBC_Remap Register- RW - 16 bits - [PCI_Reg: 8Ch]
Field Name Bits Default Description
TMKBC_Remap 15:8 00h This register defines the remap address [15:8] on the LPC
bus. There are actually four sets of such mapping. The
selection is controlled by PCI register 7Ch, bits [6:5].
00 = Set 0
01 = Set 1
10 = Set 2
11 = Set 3
There are actually four sets of such mapping (each set consists of register 84h, 88h, and 8Ch). The selection is
controlled by PCI register 7Ch, bits [6:5]. 00 = Set 0, 01 = Set 1, 10 = Set 2, 11 = Set 3. Register 7C[6:5] SHOULD
BE PROGRAMMED FIRST BEFORE 84h, 88h, AND 8Ch ARE ACCESSED.
Wide IO 2 Register- RW - 16 bits - [PCI_Reg: 90h]
Field Name Bits Default Description
IO Base Address 2 15:0 0000h 16-bit PCI IO base address for wide generic port range. 512
byte wide range. This function is enabled by PCI register
4Bh, bit 1
SPI Base_Addr Register- RW - 16 bits - [PCI_Reg: A0h]
Field Name Bits Default Description
Reserved 4:0 0h
SPI_BaseAddr 31:5 0000000h This register defines the base address for the SPI ROM
controller
3.1.3 SPI ROM Controller Registers
SPI ROM interface is a new feature added to SB600. SB600 can use SPI ROM as the BIOS ROM as well as
sharing the same physical ROM with a MAC device. In addition, SB600 can act as a SPI-LPC bridge to the
MAC device. In other words, the LAN data can be stored in the LPC/FWH ROM but the MAC can access it
through the SPI interface.
Software can communicate with the SPI ROM through the default memory or alternate program method.
Memory access to the BIOS ROM address space is automatically handled by the hardware. The SPI ROM
controller will translate the memory address onto the SPI bus and access the SPI ROM data. Any other
commands besides memory_read or memory_write to the SPI ROM will need to go through the alternate
program method. In this method, software will need to program the OpCode, SpiAddress, TxByteCount,
RxByteCount, put the data into the transmit FIFO, and then execute the command. The hardware will then
communicate with the SPI ROM using these parameters. This method is needed for the case of erasing the
SPI ROM since SPI ROM has to be erased first before any new data can be written with a separate memory
write command. This is also useful for querying the SPI status and vendor_ID register.
Register Name Offset Address
SPI_Cntrl0 00h
RestrictedCmd1 04h
RestrictedCmd2 08h
SPI_Cntrl1 0Ch
SPI_CmdValue0 10h
SPI_CmdValue1 14h
SPI_CmdValue2 18h


















