Developer’s Manual March, 2003 A-3
Intel
®
80200 Processor based on Intel
®
XScale
™
Microarchitecture
Compatibility: Intel
®
80200 Processor vs. SA-110
A.3 Architecture Deviations
A.3.1 Read Buffer
A Read Buffer is not supported on the Intel
®
80200 processor and the definition of CP15 register 9
has changed from controlling the read buffer (on SA-110) to one that controls cache/TLB lock
down (on the Intel
®
80200 processor).
The functionality of the Read Buffer on the Intel
®
80200 processor can be realized with the
existing architecture features of the Intel
®
80200 processor. The Read Buffer allowed applications
to prefetch data into the Read Buffer for future use and did not stall SA-110 during the data
prefetch. The Intel
®
80200 processor provides a PLD instruction that preloads 32 bytes of data into
the data cache. This instruction combined with the support for hit-under-miss provides similar
functionality to the Read Buffer. Note that this is for cacheable data only, so software needs to
re-map non-cacheable read-only data to cacheable before issuing the PLD instruction.
If the targeted memory region is being shared by another hardware entity, be sure to issue a
cache-invalidate (see Section 7.2.8, “Register 7: Cache Functions” on page 7-11s) before the PLD.
This ensures an incoherent copy doesn’t already exist in the Intel
®
80200 processor cache.
A.3.2 26-bit Mode
SA-110 supported 26-bit mode, the Intel
®
80200 processor does not.
A.3.3 Cacheable (C) and Bufferable (B) Encoding
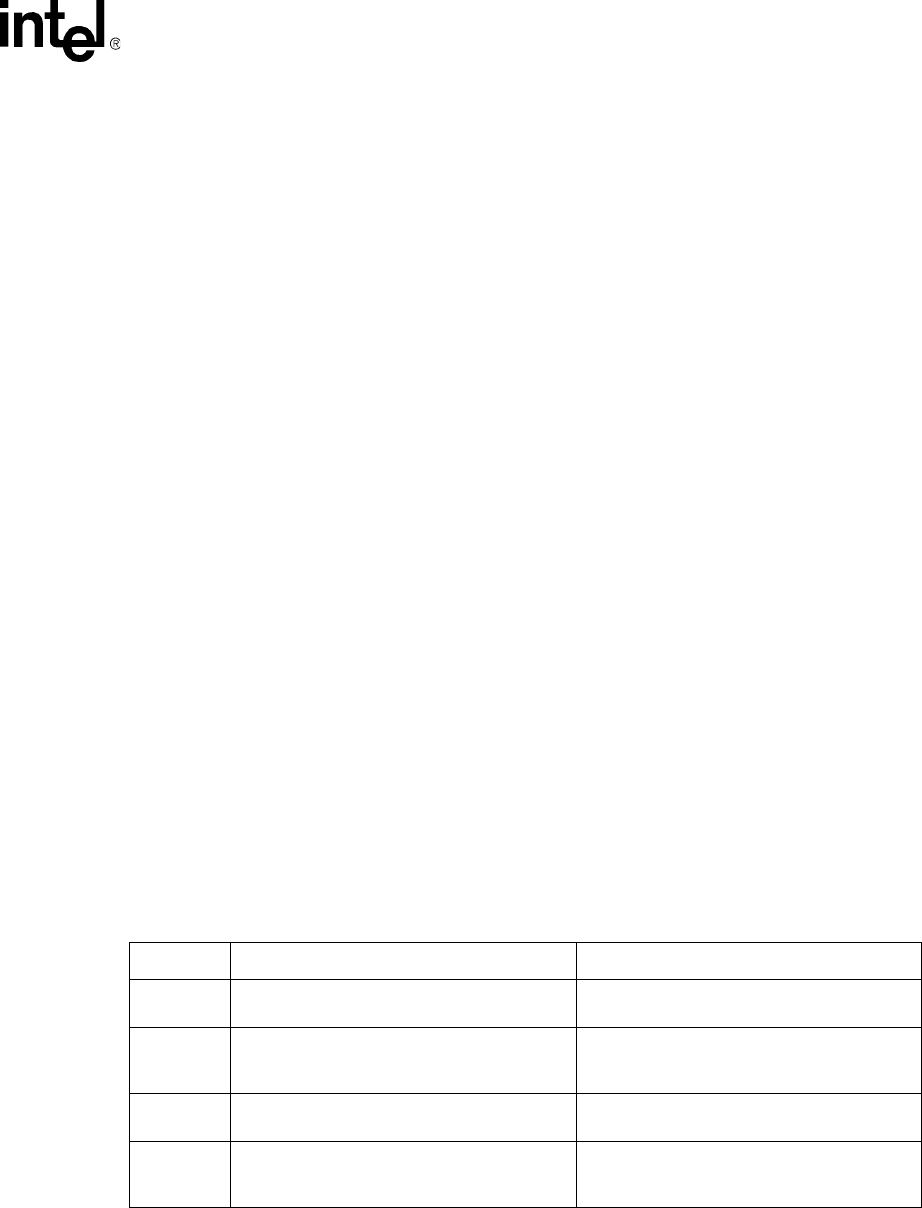
Table A-1 describes the differences in the encoding of the C and B bits for data accesses. The
Intel
®
80200 processor now follows the ARM definition of the C and B bits (when X=0). The main
difference occurs when cacheable and non-bufferable data is specified (C=1, B=0); SA-110 uses
this encoding for the mini-data cache and the Intel
®
80200 processor uses this encoding to specify
write-through caching. Another subtle difference is for C=0, B=1, where the Intel
®
80200
processor coalesces and stores in the write buffer and SA-110 does not.
Table A-1. C and B encoding
Encoding SA-110 Function Intel
®
80200 Processor Function
C=1,B=1
Cacheable in data cache; store misses can
coalesce in write buffer
Cacheable in data cache, store misses can
coalesce in write buffer
C=1,B=0
Cacheable in mini-data cache; store misses
can coalesce in write buffer
Cacheable in data cache, with a write-through
policy. Store misses can coalesce in write
buffer
C=0,B=1
Non-cacheable; no coalescing in write buffer,
but can wait in write buffer
Non-cacheable; stores can coalesce in the
write buffer
C=0,B=0
Non-cacheable; no coalescing in the write
buffer, SA-110 stalls until this transaction is
done
Non-cacheable, no coalescing in the write
buffer, Intel
®
80200 processor does stall until
the operation is complete.


















