7-16 March, 2003 Developer’s Manual
Intel
®
80200 Processor based on Intel
®
XScale
™
Microarchitecture
Configuration
7.2.13 Register 13: Process ID
The Intel
®
80200 processor supports the remapping of virtual addresses through a Process ID
(PID) register. This remapping occurs before the instruction cache, instruction TLB, data cache and
data TLB are accessed. The PID register controls when virtual addresses are remapped and to what
value.
The PID register is a 7-bit value that is ORed with bits 31:25 of the virtual address when they are
zero. This effectively remaps the address to one of 128 “slots” in the 4 Gbytes of address space. If
bits 31:25 are not zero, no remapping occurs. This feature is useful for operating system
management of processes that may map to the same virtual address space. In those cases, the
virtually mapped caches on the Intel
®
80200 processor would not require invalidating on a process
switch.
7.2.13.1 The PID Register Affect On Addresses
All addresses generated and used by User Mode code are eligible for being “PIDified” as described
in the previous section. Privileged code, however, must be aware of certain special cases in which
address generation does not follow the usual flow.
The PID register is not used to remap the virtual address when accessing the Branch Target Buffer
(BTB). Any writes to the PID register invalidate the BTB, which prevents any virtual addresses
from being double mapped between two processes.
A breakpoint address (see Section 7.2.14, “Register 14: Breakpoint Registers” on page 7-17) must
be expressed as an MVA when written to the breakpoint register. This means the value of the PID must
be combined appropriately with the address before it is written to the breakpoint register. All virtual
addresses in translation descriptors (see Chapter 3, “Memory Management”) are MVAs.
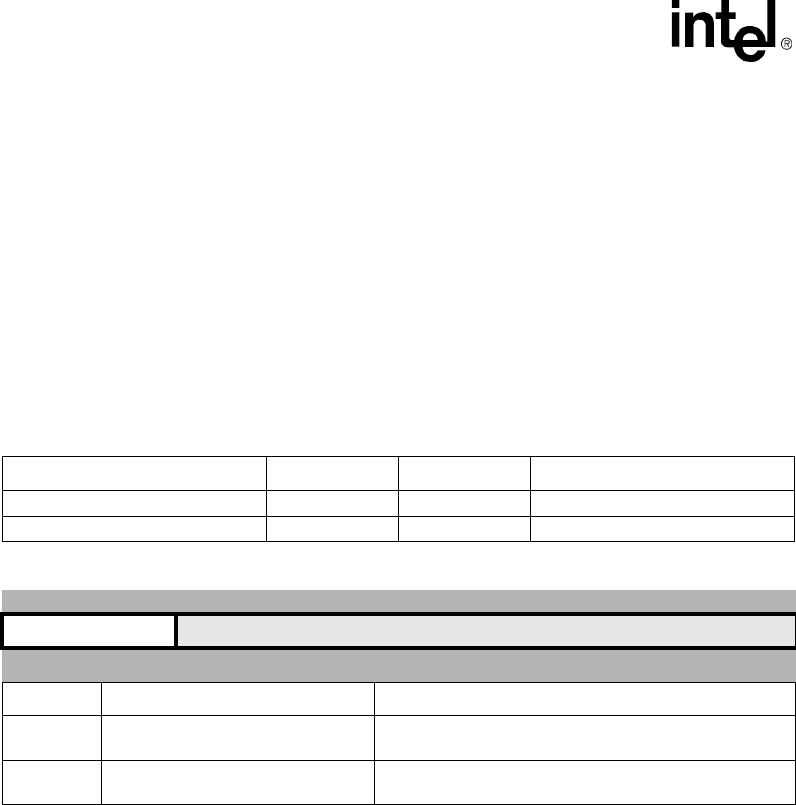
Table 7-17. Accessing Process ID
Function opcode_2 CRm Instruction
Read Process ID Register 0b000 0b0000 MRC p15, 0, Rd, c13, c0, 0
Write Process ID Register 0b000 0b0000 MCR p15, 0, Rd, c13, c0, 0
Table 7-18. Process ID Register
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Process ID
reset value: 0x0000,0000
Bits Access Description
31:25 Read / Write
Process ID - This field is used for remapping the virtual
address when bits 31-25 of the virtual address are zero.
24:0 Read-as-Zero / Write-as-Zero
Reserved - Should be programmed to zero for future
compatibility


















