Developer’s Manual March, 2003 2-5
Intel
®
80200 Processor based on Intel
®
XScale
™
Microarchitecture
Programming Model
MIA does not support unsigned multiplication; all values in Rs and Rm are interpreted as signed
data values. MIA is useful for operating on signed 16-bit data that was loaded into a general
purpose register by LDRSH.
The instruction is only executed if the condition specified in the instruction matches the condition
code status.
The MIAPH instruction performs two16-bit signed multiplies on packed half word data and
accumulates these to a single 40-bit accumulator. The first signed multiplication is performed on
the lower 16 bits of the value in register Rs with the lower 16 bits of the value in register Rm. The
second signed multiplication is performed on the upper 16 bits of the value in register Rs with the
upper 16 bits of the value in register Rm. Both signed 32-bit products are sign extended and then
added to the value in the 40-bit accumulator (acc0).
The instruction is only executed if the condition specified in the instruction matches the condition
code status.
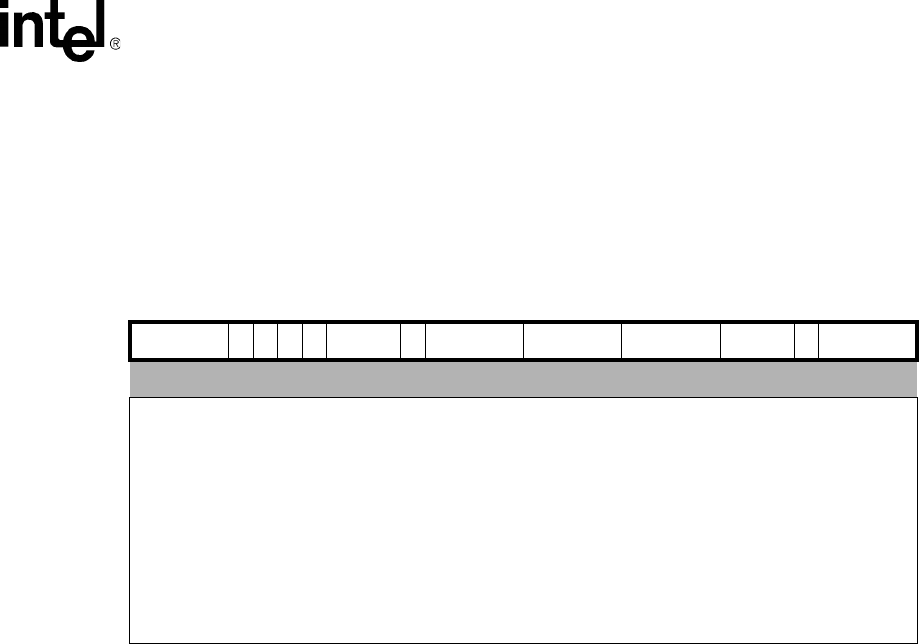
Table 2-3. MIAPH{<cond>} acc0, Rm, Rs
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
cond 111000101000 Rs 00000001 Rm
Operation: if ConditionPassed(<cond>) then
acc0 = sign_extend(Rm[31:16] * Rs[31:16]) +
sign_extend(Rm[15:0] * Rs[15:0]) +
acc0[39:0]
Exceptions:none
Qualifiers Condition Code
S bit is always cleared; no condition code flags are updated
Notes: Instruction timings can be found
in Section 14.4.4, “Multiply Instruction Timings” on page 14-6.
Specifying R15 for register Rs or Rm has unpredictable results.
acc0 is defined to be 0b000 on 80200


















