103
3.13 DMA Suppression
3.13 DMA Suppression
If an interrupt with a higher priority occurs during DMA transfer, the FR series
interrupts DMA transfer and branches to the corresponding interrupt routine. This
feature remains effective as long as an interrupt request continues. When the
interrupt cause is cleared, the suppression feature is canceled and DMA transfer
resumes in the interrupt processing routine.
It a DMA transfer is not to be resumed, use the DMA suppression function after the
cause of the interrupt is resolved by the DMA transfer interrupt processing routine.
The DMA suppression function is activated by writing a value other than 0 to the DMA
suppression register and is deactivated by writing 0 to the register.
■
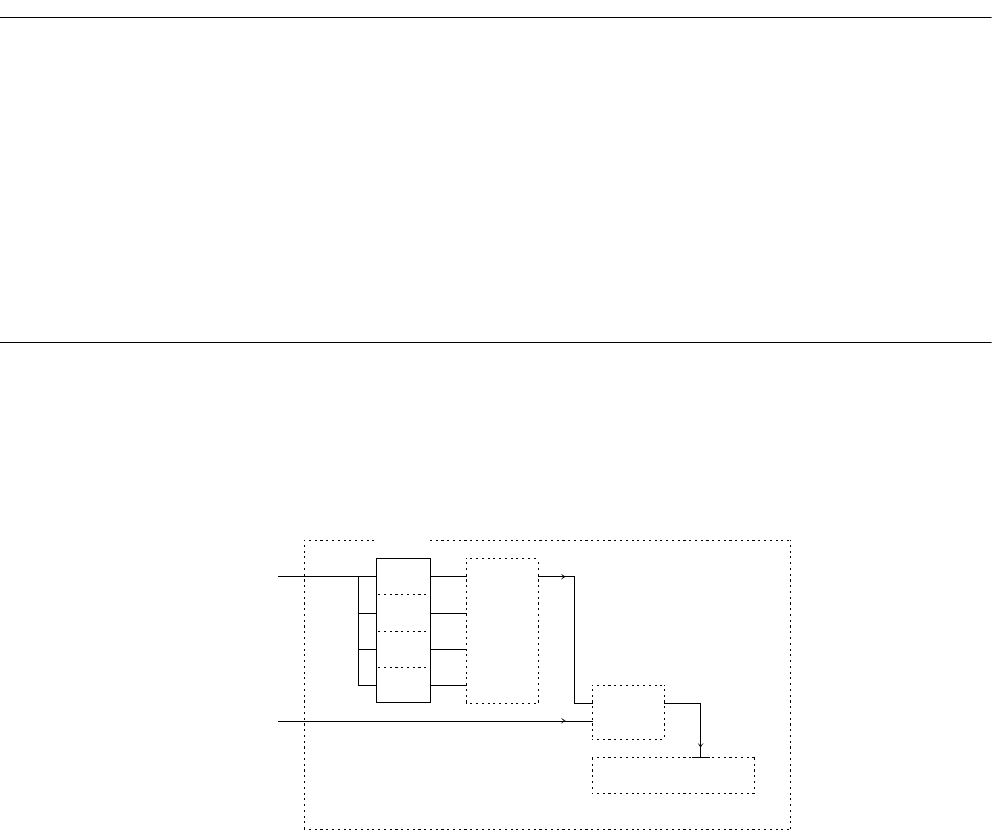
DMA Suppression Circuit Block Diagram
Figure 3.13.1 is a block diagram of the DMA suppression circuit.
Figure 3.13-1 DMA Suppression Circuit Block Diagram
■
Setting for DMA Suppression
The DMA suppression function is used mainly in the interrupt processing routine.
In the interrupt processing routing, the function increments the value in the DMA suppression
register by one before the interrupt cause is cleared, thereby preventing DMA transfer
thereafter. When the interrupt processing is finished, the function decrements the register value
by one before control returns from the interrupt processing routine. In the case of multiple
interrupts, decrementing the value by one does not clear the value in the DMA suppression
register and so DMA transfer remains suppressed. In the case of a single interrupt,
decrementing the value by one clears the register value and so DMA requests are soon
enabled.
PDRR
D3
D2
D1
D0 .nor.
.and.
Internal bus
DMA request
State transition control circuit