218
CHAPTER 6 EXTERNAL INTERRUPT/NMI CONTROLLER
6.7 Nonmaskable Interrupt (NMI) Operation
NMI is the interrupt with the highest priority among other user interrupts. It can only
be masked during the period from immediately after a reset to the completion of the
ILM setting.
■
NMI Operation
NMI is accepted as follows:
• Normal state: Falling edge
• Stop state: "L" level
NMI can be used to cancel the stop state. When the "L" level is input in the stop state, the stop
state is canceled and the oscillation stabilization time is spent.
If the NMIX pin receives the "H" level within the oscillation stabilization time, the NMI cause is
lost and NMI processing is not performed after the operation restarts. When NMI processing is
desired after the stop state is canceled, keep the NMIX pin at the "L" level and return it to the
"H" level within the NMI processing routine.
The NMI request detection block has an NMI bit, which is set by an NMI request and can be
cleared only when the NMI interrupt itself is received or during a reset. The NMI bit cannot be
read or written.
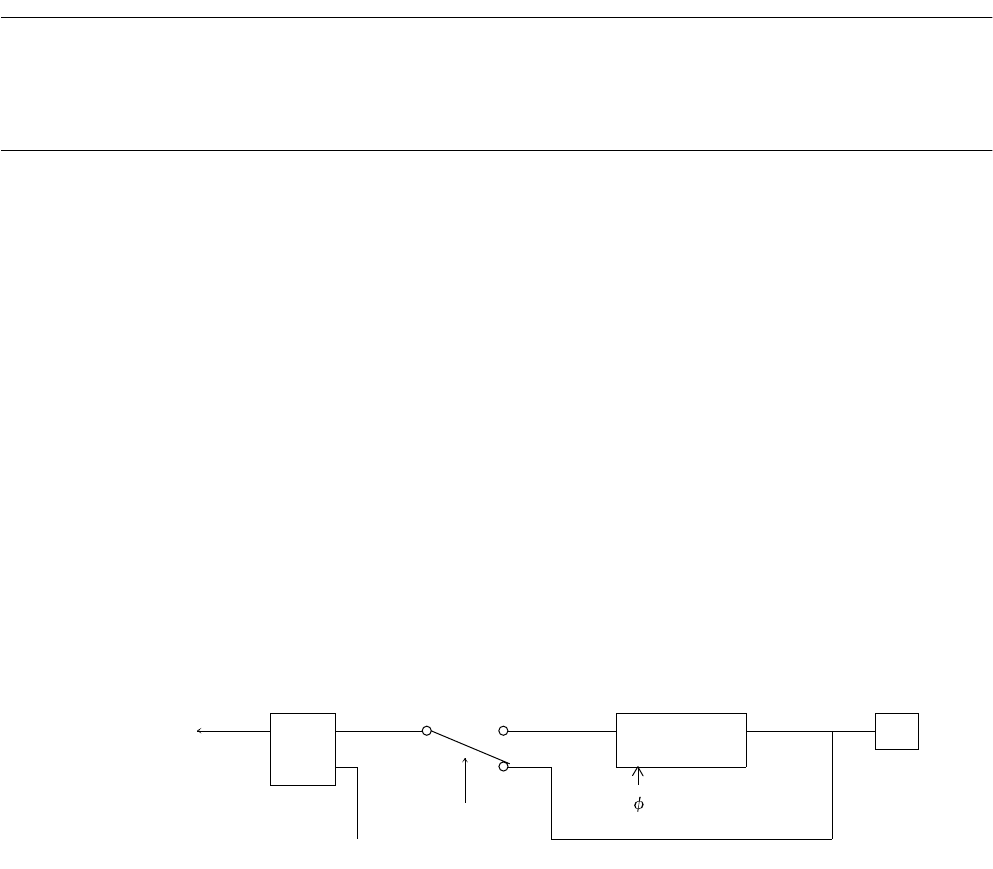
Figure 6.7-1 shows the NMI request detection block.
Figure 6.7-1 NMI Request Detection Block
<Note>
Since the interrupt cause is automatically cleared when NMI is accepted, DMA cannot be
controlled. When the NMI is accepted, DMA is retransferred, and when DMA transfer is
finished, NMI processing is performed.
0
QSX NMIX
R
1
STOP
clear (RST,interrupt acknowledge)
NMI request
(canceling the stop state)
Detection of
falling edge