62
CHAPTER 2 CPU
2.8.7 Multiple EIT Processing
When multiple EIT events occur concurrently, the CPU selects one EIT event, accepts
it, executes the EIT sequence, and then detects another EIT event. It repeats this
operation for all EIT events. When no more acceptable EIT event is detected, the CPU
executes the instruction of the handler of the EIT event accepted last.
When multiple EIT events occur concurrently, the execution order of the handlers of
individual events is determined according to the following two factors:
• Priority for EIT event acceptance
• Mode of masking other EIT events after one is accepted
■
Priority for EIT Event Acceptance
The priority for EIT event acceptance is the order in which an EIT event to be accepted for an
EIT sequence is selected. In the EIT sequence, PS and PC are saved, PC is updated (as
needed,) and the other EIT events are masked.
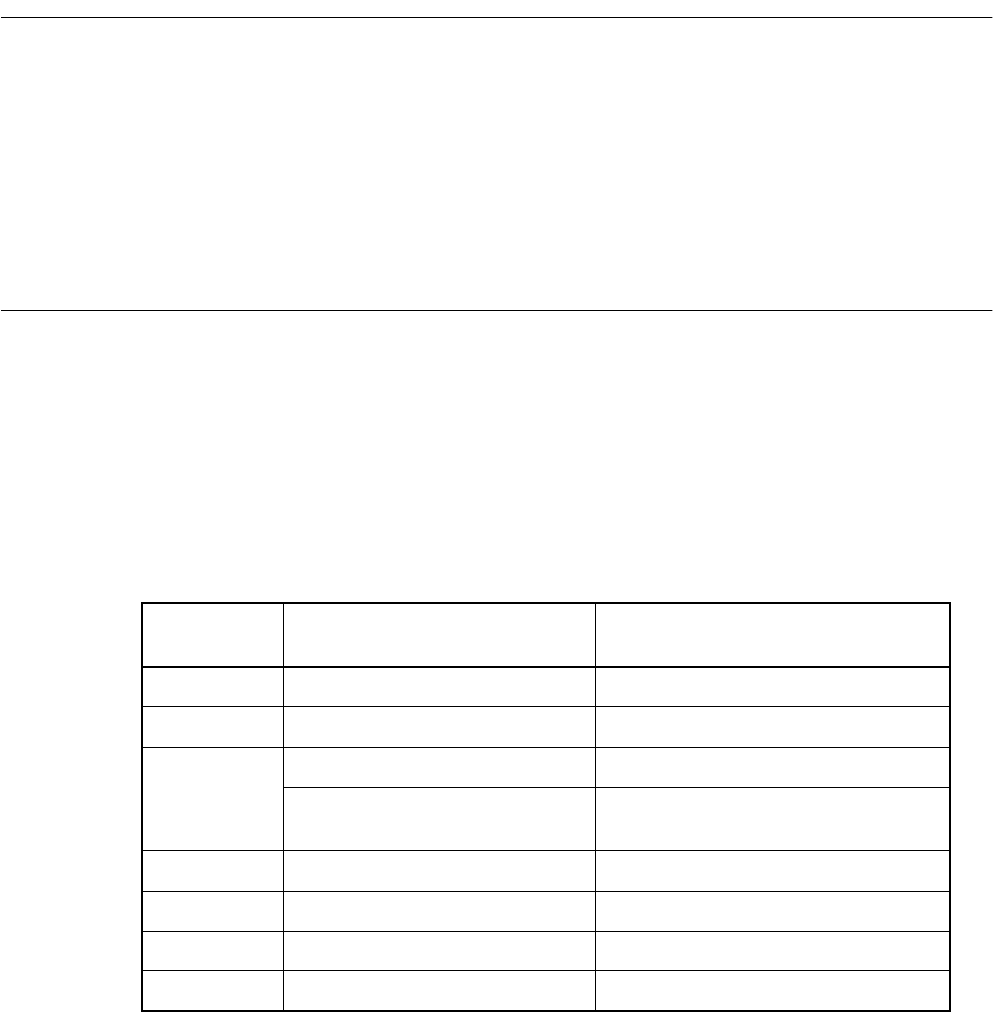
The handler of an EIT event accepted earlier is not always executed first. Table 2.8.4 lists the
priority levels for acceptance of individual EIT events.
After an EIT event is accepted and mask processing is performed for other events, the handlers
of the concurrent EIT events are executed in the order shown in Table 2.8.5.
Table 2.8-4 Priority for EIT Event Acceptance and Masking Other Events
Acceptance
priority
EIT event Masking other events
1 Reset The other events are discarded.
2 Undefined-instruction exception Cancel
3 INT instruction I flag=0
Coprocessor nonexistent trap
Coprocessor error trap
None
4 User interrupt ILM = Level of accepted event
5 NMI (for user) ILM = 15
6 Step-trace-trap ILM = 4
7 INTE instruction ILM = 4