237
8.8 Example of Using the Hold Request Cancel Request Function (HRCR)
■
Hold Request Cancel Request Sequence
❍
Example of interrupt routine
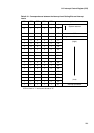
Figure 8.8-2 Example of Timing for Hold Request Cancel Request Sequence (Interrupt Level: HRCL > a)
The interrupt level changes when an interrupt request is issued. If the level is higher than that
set in the HRCL register, HRCR is activated for DMA, thereby causing DMA to cancel the hold
request, and the CPU returns from the hold state and performs interrupt processing. The
interrupt routine increments PDRR 1 to clear the interrupt cause 2, thereby changing the
interrupt level and rendering HRCR inactive. Accordingly, HRCR is inactivated to allow DMA to
issue a hold request, but the hold request is interrupted because PDRR is not 0. The hold
request is transmitted to the CPU to allow DMA transfer again only after PDRR is decremented
3.
❍
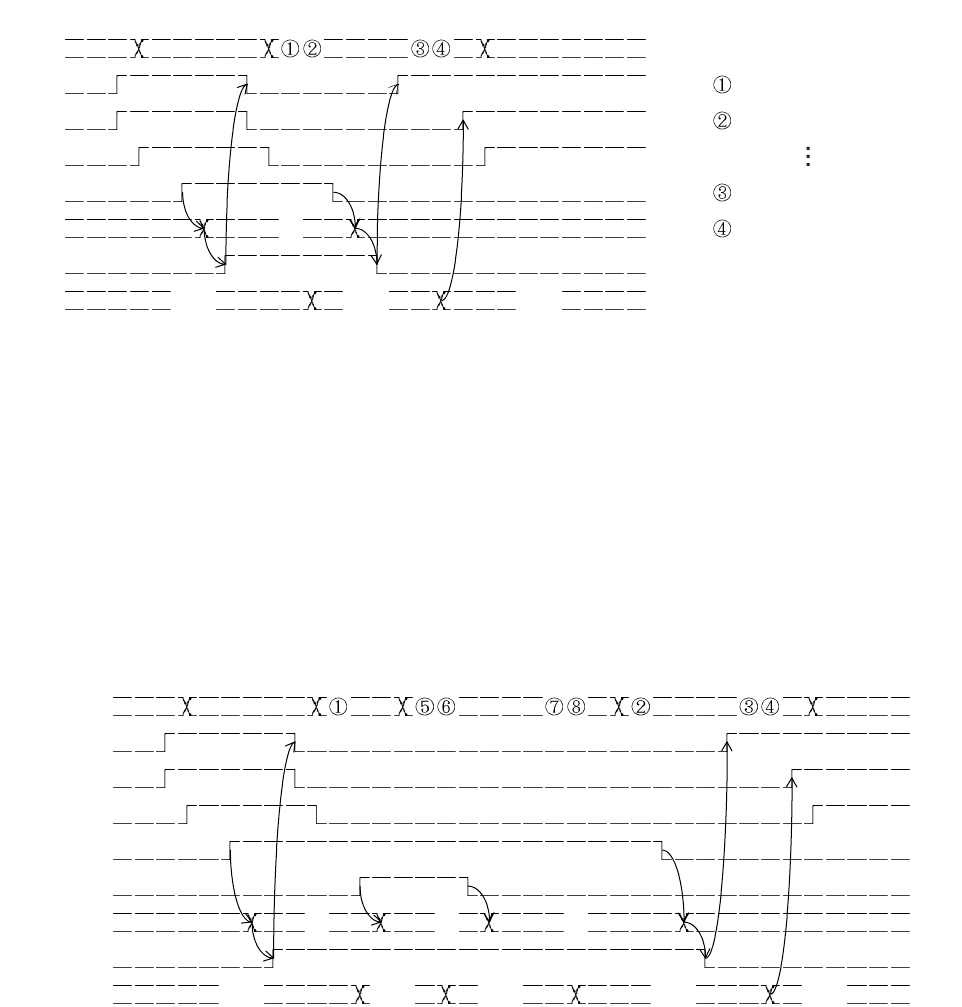
Example of multiple-interrupt routine
Figure 8.8-3 Example of Timing for Hold Request Cancel Request Sequence (Interrupt Level: HRCL > a
> b)
RUN
CPU
DHRQ
HRQ
HACK
IRQ
LEVEL a RETI
HRCR
PDRR 0000 0001 0000
Bus hold
Interrupt processing Bus hold (DMA transfer)
Example of interrupt routine
Incrementing PDRR
Clearing the interrupt cause
Decrementing PDRR
CPU
DHRQ
HRQ
HACK
IRQ1
IRQ2
LEVEL a b a
HRCR
PDRR 0000 0001 0002 0001 0000
RUN
Bus hold
Interrupt I
Interrupt processing II
Interrupt processing I
Bus hold