31
2.2 Internal Architecture
2.2 Internal Architecture
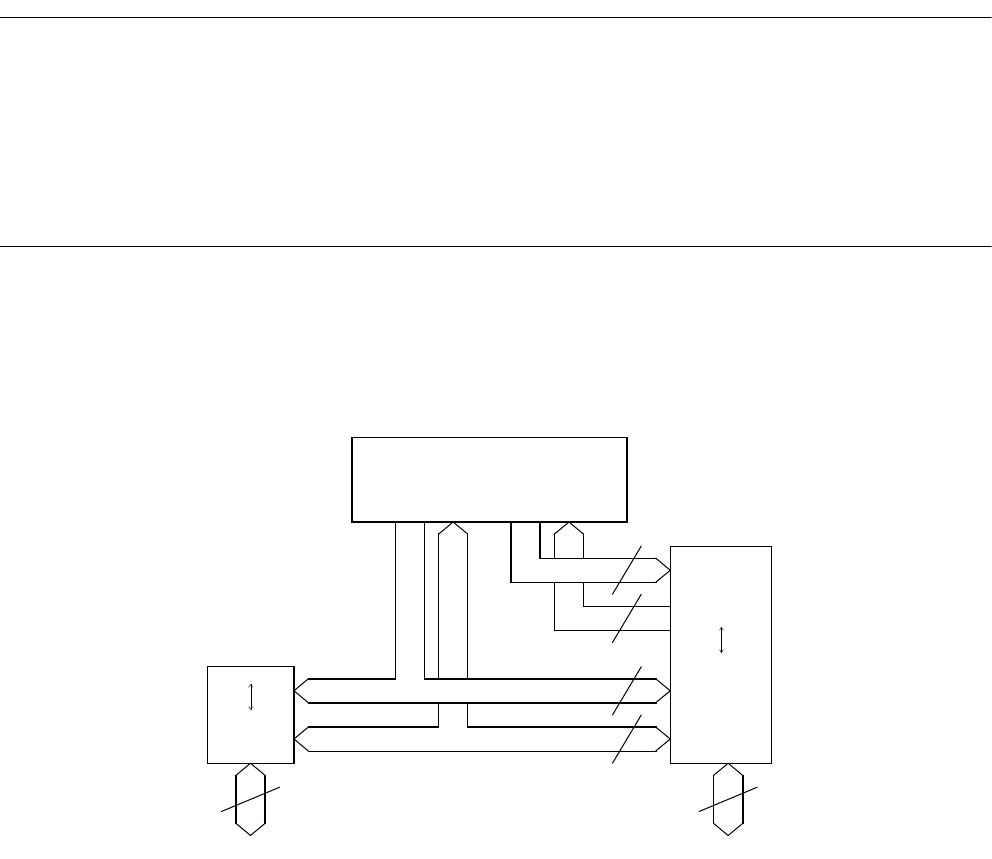
The FR CPU uses the Harvard architecture in which the instruction bus and data bus
are independent of each other.
The "32 bits <--> 16 bits" bus converter is connected to the data bus (D-BUS) to
implement the interface between the CPU and peripheral resources. The "Harvard <-->
Princeton" bus converter is connected to both I-BUS and D-BUS to implement the
interface between the CPU and bus controller.
■
Internal Architecture
Figure 2.2.1 shows the internal architecture.
Figure 2.2-1 Internal Architecture
❍
CPU
The CPU is a compact implement of the 32-bit RISC FR architecture.
It uses a five-stage instruction pipeline system to execute one instruction per cycle. The
pipeline consists of the following five stages:
• Instruction fetch (IF): Outputs an instruction address and fetches the instruction.
• Instruction decode (ID): Decodes the fetched instruction and also reads registers.
• Execution (EX): Executes operation.
• Memory access (MA): Accesses memory for loading or storing data.
• Write back (WB): Writes the operation results (or loaded memory data) to registers.
Figure 2.2.2 shows the instruction pipeline.
32
I-ADDR
16
I-DATA
32
32bit
D-ADDR
16bit
32
D-DATA
16 32
FR CPU
D-BUS
I-BUS
R-BUS
C-BUS
Bus
converter
Bus
converter
Resources
Harvard
Princeton
Bus controller


















