276
CHAPTER 11 A/D CONVERTER (Successive approximation type)
11.4 A/D Converter Operation
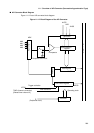
The A/D converter operates in successive approximation mode and features a 10-bit
resolution.
The A/D converter has only one register (16 bits) to store the conversion results.
Therefore, the data register (ADCR) is updated whenever conversion is completed. For
performing continuous conversion, DMA transfer should be used.
■
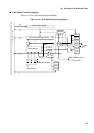
A/D Converter Operation Modes
In single conversion mode, the A/D converter sequentially converts the analog inputs specified
by the ANS and ANE bits of the ADCS register and stops operation after converting the analog
input from the end channel specified by the ANE bits.
If the start and end channels are the same (ANS = ANE), the analog input from only one
channel is converted.
❍
Single conversion mode
In single mode, analog input set by the ANS bit and ANE bit of ADCS is converted in order.
When the conversion of the end channel set by the ANE bit is completed, the A/D converter
stops its operation.
If the start channel and the end channel are the same (ANS=ANE), one channel conversion is
adopted.
Example:
ANS = 000, ANE = 011
Start --> AN0 --> AN1 --> AN2 --> AN3 --> End
ANS = 010, ANE = 010
Start --> AN2 --> End
❍
Continuous conversion mode
In continuous conversion mode, the A/D converter sequentially converts the analog inputs
specified by the ANS and ANE bits of the ADCS register. When conversion is finished up to the
end channel specified by the ANE bits, the converter returns to the ANS analog input and
continues A/D conversion.
If the start and end channels are the same (ANS = ANE), conversion of the analog input from
only one channel is repeated.
Example:
ANS = 000, ANE = 011
Start --> AN0 --> AN1 --> AN2 --> AN3 --> AN0 ... --> iteration
ANS = 010, ANE = 010
Start --> AN2 --> AN2 --> AN2 ... --> iteration