190
CHAPTER 4 BUS INTERFACE
4.17.19 Hyper DRAM Interface
This section provides a hyper DRAM interface timing chart.
■
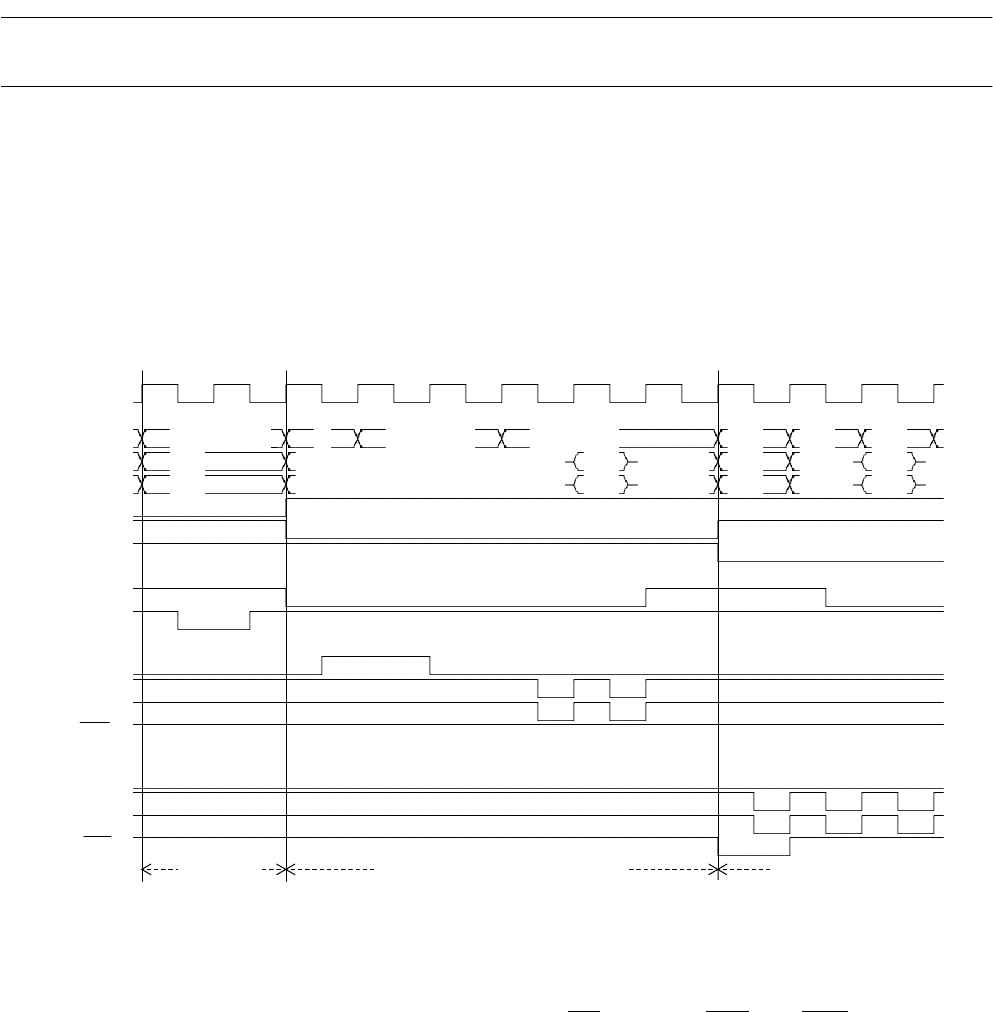
Hyper DRAM Interface Timing Chart
❍
Combination of hyper DRAM and basic bus cycle, CS switch-over
Figure 4.17-34 Example of Hyper DRAM Interface Timing Chart
[Explanation of operation]
• When a bus cycle starts from a high-speed page, RDX in a read cycle goes down to "L" from
the falling edge of Q4HR and is negated when the Q4HR cycle ends. In a write cycle, it
goes down to "L" from the rising edge of WE
(including WEL and WEH) Q4HW and is
negated when the Q4HW cycle ends.
• CS4X and CS5X change at the same time as the output address. When a bus cycle starts
from a high-speed page, they change from the Q4HR and Q4HW cycles as with the column
address.
BA1 BA2 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4HR Q4HR Q4HW Q4HR Q4HR
CLK
A24-00 CS2X basic bus X row.adr. col.adr. col. col. col.
D31-24
D23-16
CS2X
CS4X
CS5X
RDX
WR0X
CS4:RAS
CS4:CASL
CS4:CASH
CS4:WE
CS5:RAS
CS5:CASL
CS5:CASH
CS5:WE
CS2
nomal
CS4Hyper DRAM read CS5 Hyper DRAM
write/read
Write
Read
Write
Read
Write
Write Read
Read
Idle


















