V DMA BLOCK: HSDMA (High-Speed DMA)
S1C33L03 FUNCTION PART EPSON B-V-2-9
A-1
B-V
HSDMA
Operation of HSDMA
An HSDMA channel starts data transfer by the selected trigger factor.
Make sure that transfer conditions and a trigger factor are set and the HSDMA channel is enabled before starting a
DMA transfer.
Operation in Dual-Address Mode
In dual-address mode, both the source and destination addresses are accessed according to the bus condition set by
the BCU.
HSDMA has three transfer modes, in each of which data transfer operates differently. The following describes the
operation of HSDMA in each transfer mode.
Single transfer mode
The channel for which DxMOD in control information is set to "00" operates in single transfer mode. In this
mode, a transfer operation invoked by one trigger is completed after transferring one data unit of the size set
by DATSIZEx. If a data transfer needs to be performed a number of times as set by the transfer counter, an
equal number of triggers are required.
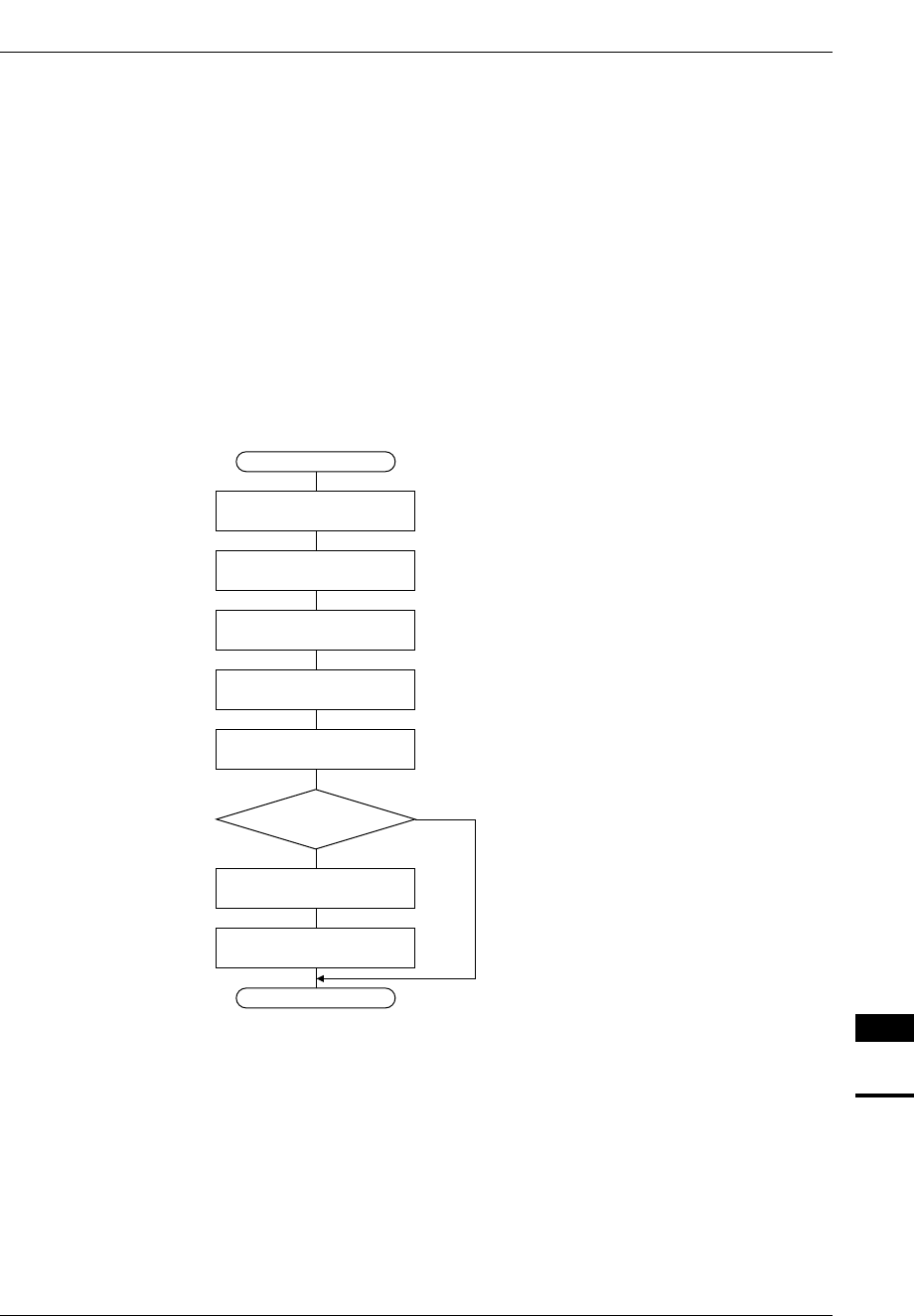
The operation of HSDMA in single transfer mode is shown by the flow chart in Figure 2.3.
START
END
Data read from source
(1 byte or 1 half word)
Clear trigger flag HSx_TF
to accept next trigger
Clear HSDMA enable bit
HSx_EN
Data write to destination
(1 byte or 1 half word)
Transfer counter - 1
Set interrupt factor flag
FHDMx
Transfer
counter = 0
N
Y
Increment/decrement
address ∗
∗: according to SxIN/DxIN
settings
Figure 2.3 Operation Flow in Single Transfer Mode
(1) When a trigger is accepted, the trigger flag HSx_TF is cleared and then data of the size set in the control
information is read from the source address.
(2) The read data is written to the destination address.
(3) The addresses are incremented or decremented according to the SxIN/DxIN settings.
(4) The transfer counter is decremented.
(5) The HSDMA enable bit HSx_EN is cleared and HSDMA interrupt factor flag in ITC is set when the
transfer counter reaches 0 (when DINTENx = "1").


















