V DMA BLOCK: HSDMA (High-Speed DMA)
S1C33L03 FUNCTION PART EPSON B-V-2-15
A-1
B-V
HSDMA
Interrupt Function of HSDMA
The DMA controller can generate an interrupt when the transfer counter in each HSDMA channel reaches 0.
Furthermore, channels 0 and 1 can invoke IDMA using their interrupt factor.
Control registers of the interrupt controller
Table 2.3 shows the control registers of the interrupt controller that are provided for each channel.
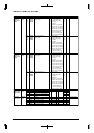
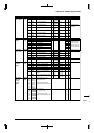
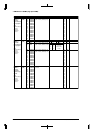
Table 2.3 Control Registers of Interrupt Controller
Channel Interrupt factor flag Interrupt enable register Interrupt priority register
Ch. 0 FHDM0(D0/0x40281) EHDM0(D0/0x40271) PHSD0L[2:0](D[2:0]/0x40263)
Ch. 1 FHDM1(D1/0x40281) EHDM1(D1/0x40271) PHSD1L[2:0](D[6:4]/0x40263)
Ch. 2 FHDM2(D2/0x40281) EHDM2(D2/0x40271) PHSD2L[2:0](D[2:0]/0x40264)
Ch. 3 FHDM3(D3/0x40281) EHDM3(D3/0x40271) PHSD3L[2:0](D[6:4]/0x40264)
The HSDMA controller sets the HSDMA interrupt factor flag to "1" when the transfer counter reaches 0 after
completing a series of HSDMA transfers. If the corresponding bit of the interrupt enable register is set to "1"
at this time, an interrupt request is generated. Interrupts can be disabled by leaving the interrupt enable
register bit set to "0". The HSDMA interrupt factor flag is always set to "1" when the data transfer in each
channel is completed no matter what value the interrupt enable register bit is set to. (This is true even when it
is set to "0".)
The interrupt priority register sets an interrupt priority level (0 to 7). An interrupt request to the CPU is
accepted only when there is no other interrupt request of higher priority. Furthermore, it is only when the
PSR's IE bit = "1" (interrupt enable) and the set value of IL is smaller than the HSDMA interrupt level which
is set in the interrupt priority register that the CPU actually accepts a HSDMA interrupt. For details about the
interrupt control register and for the device operation when an interrupt occurs, refer to "ITC (Interrupt
Controller)".