142
CHAPTER 8 LOW-POWER CONSUMPTION MODE
8.4 CPU Intermittent Operation Mode
This mode is used for intermittent operation of the CPU while operation clock is
supplied to the CPU and peripheral functions. The purpose of this mode is to reduce
power consumption.
■ CPU Intermittent Operation Mode
This mode halts the supply of the clock pulse to the CPU for a certain period. The halt occurs after the
execution of every instruction that accesses a register, internal memory, I/O, peripheral functions, or the
external bus. Internal bus cycle activation is therefore delayed. While high-speed peripheral clock pulses
are supplied to peripheral functions, the execution speed of the CPU is reduced, thereby enabling low-
power consumption processing.
• The low-power consumption mode control register (LPMCR: CG1 and CG0) is used to select the
number of machine cycles that halts the clock supplied to the CPU.
• Instruction execution time in the CPU intermittent operation mode can be calculated. A correction value
should be obtained by multiplying the execution count of instructions that access a register, internal
memory, internal peripheral functions, or the external bus by the number of clock pulses per halt cycle.
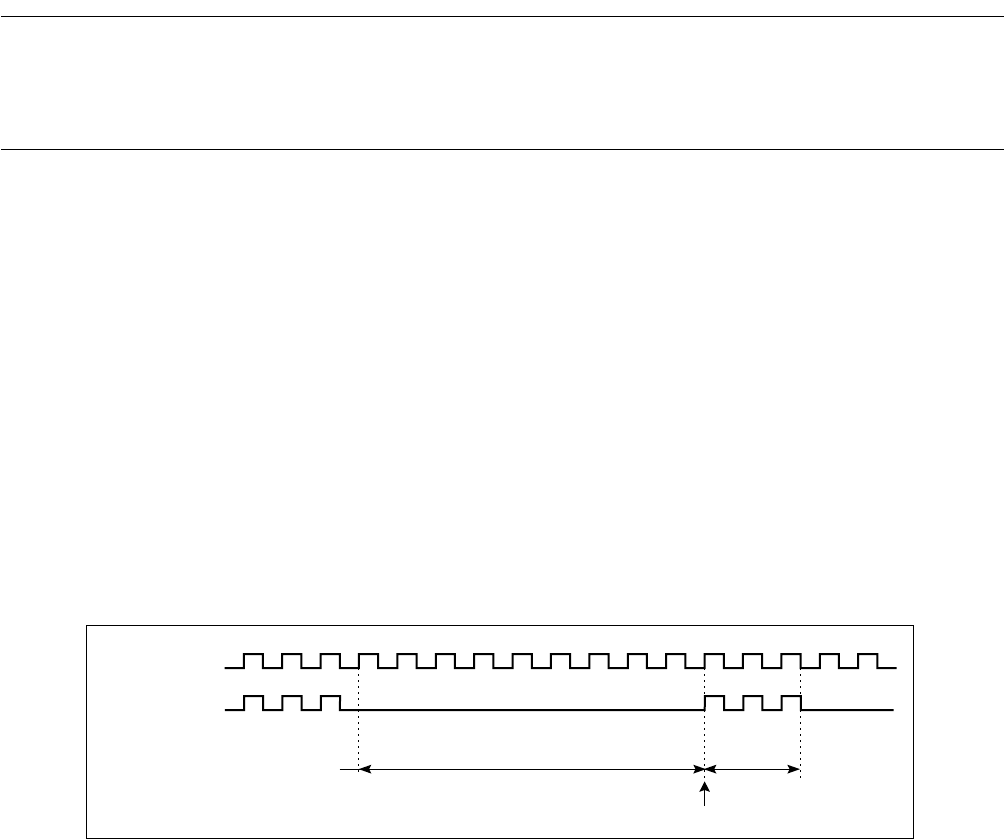
Add this corrective value to the normal execution time. Figure 8.4-1 shows the operating clock pulses
during the CPU intermittent operation mode.
Figure 8.4-1 Clock Pulses during the CPU Intermittent Operation Mode
Peripheral clock
CPU clock
1-instruction
execution
cycle
Halt cycle
Internal bus starts


















