546
CHAPTER 24 512K-BIT FLASH MEMORY
24.7.2 Writing Data
This section describes the procedure for issuing the Write command to write data to the
flash memory.
■ Writing Data to the Flash Memory
The data write automatic algorithm of the flash memory can be started by sending the Write command in
the command sequence table (see Table 24.5-1 ) continuously to the target sector in the flash memory.
When data write to the target address is completed in the fourth cycle, the automatic algorithm and
automatic write are started.
●
Specifying addresses
Only even addresses can be specified as the write addresses specified in a write data cycle. Odd addresses
cannot be written correctly. That is, writing to even addresses must be done in units of word data.
Writing can be done in any order of addresses. However, the Write command writes only data of one word
for each execution.
●
Notes on writing data
Writing cannot return data 0 to data 1. When data 1 is written to data 0, the data polling algorithm (DQ7) or
toggle operation (DQ6) does not terminate and the flash memory elements are determined to be faulty. If
the time prescribed for writing is thus exceeded, the timing limit exceeded flag (DQ5) is determined to be
an error. Otherwise, the data is viewed as if dummy data 1 had been written. However, when data is read in
the read/reset state, the data remains 0. Data 0 can be set to data 1 only by erase operations.
All commands are ignored during execution of the automatic write algorithm. If a hardware reset is started
during writing, the data of the written addresses will be unpredictable.
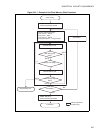
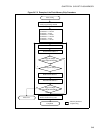
■ Writing to the Flash Memory
Figure 24.7-1 is an example of the procedure for writing to the flash memory. The hardware sequence flags
(see "24.6 Confirming the Automatic Algorithm Execution State") can be used to determine the state of the
automatic algorithm in the flash memory. Here, the data polling flag (DQ7) is used to confirm that writing
has terminated.
The data read to check the flag is read from the address written to last.
The data polling flag (DQ7) changes at the same time that the timing limit exceeded flag (DQ5) changes.
For example, even if the timing limit exceeded flag (DQ5) is 1, the data polling flag bit (DQ7) must be
rechecked.
Also for the toggle bit flag (DQ6), the toggle operation stops at the same time that the timing limit
exceeded flag bit (DQ5) changes to 1. The toggle bit flag (DQ6) must therefore be rechecked.